Page 1084 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1084
1070 SECTION X Special Topics
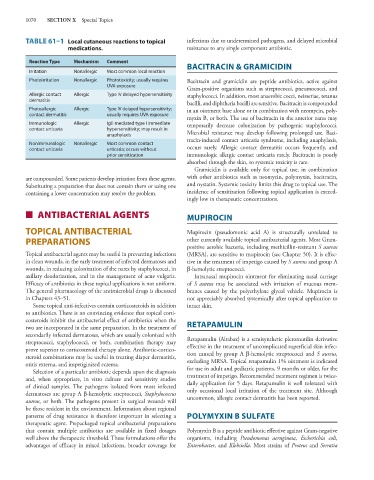
TABLE 61–1 Local cutaneous reactions to topical infections due to undetermined pathogens, and delayed microbial
medications. resistance to any single component antibiotic.
Reaction Type Mechanism Comment
BACITRACIN & GRAMICIDIN
Irritation Nonallergic Most common local reaction
Photoirritation Nonallergic Phototoxicity; usually requires Bacitracin and gramicidin are peptide antibiotics, active against
UVA exposure
Gram-positive organisms such as streptococci, pneumococci, and
Allergic contact Allergic Type IV delayed hypersensitivity staphylococci. In addition, most anaerobic cocci, neisseriae, tetanus
dermatitis bacilli, and diphtheria bacilli are sensitive. Bacitracin is compounded
Photoallergic Allergic Type IV delayed hypersensitivity; in an ointment base alone or in combination with neomycin, poly-
contact dermatitis usually requires UVA exposure
myxin B, or both. The use of bacitracin in the anterior nares may
Immunologic Allergic IgE-mediated type I immediate temporarily decrease colonization by pathogenic staphylococci.
contact urticaria hypersensitivity; may result in
anaphylaxis Microbial resistance may develop following prolonged use. Baci-
tracin-induced contact urticaria syndrome, including anaphylaxis,
Nonimmunologic Nonallergic Most common contact
contact urticaria urticaria; occurs without occurs rarely. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs frequently, and
prior sensitization immunologic allergic contact urticaria rarely. Bacitracin is poorly
absorbed through the skin, so systemic toxicity is rare.
Gramicidin is available only for topical use, in combination
are compounded. Some patients develop irritation from these agents. with other antibiotics such as neomycin, polymyxin, bacitracin,
Substituting a preparation that does not contain them or using one and nystatin. Systemic toxicity limits this drug to topical use. The
containing a lower concentration may resolve the problem. incidence of sensitization following topical application is exceed-
ingly low in therapeutic concentrations.
■ ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS MUPIROCIN
TOPICAL ANTIBACTERIAL Mupirocin (pseudomonic acid A) is structurally unrelated to
PREPARATIONS other currently available topical antibacterial agents. Most Gram-
positive aerobic bacteria, including methicillin-resistant S aureus
Topical antibacterial agents may be useful in preventing infections (MRSA), are sensitive to mupirocin (see Chapter 50). It is effec-
in clean wounds, in the early treatment of infected dermatoses and tive in the treatment of impetigo caused by S aureus and group A
wounds, in reducing colonization of the nares by staphylococci, in β-hemolytic streptococci.
axillary deodorization, and in the management of acne vulgaris. Intranasal mupirocin ointment for eliminating nasal carriage
Efficacy of antibiotics in these topical applications is not uniform. of S aureus may be associated with irritation of mucous mem-
The general pharmacology of the antimicrobial drugs is discussed branes caused by the polyethylene glycol vehicle. Mupirocin is
in Chapters 43–51. not appreciably absorbed systemically after topical application to
Some topical anti-infectives contain corticosteroids in addition intact skin.
to antibiotics. There is no convincing evidence that topical corti-
costeroids inhibit the antibacterial effect of antibiotics when the
two are incorporated in the same preparation. In the treatment of RETAPAMULIN
secondarily infected dermatoses, which are usually colonized with
streptococci, staphylococci, or both, combination therapy may Retapamulin (Altabax) is a semisynthetic pleromutilin derivative
prove superior to corticosteroid therapy alone. Antibiotic-cortico- effective in the treatment of uncomplicated superficial skin infec-
steroid combinations may be useful in treating diaper dermatitis, tion caused by group A β-hemolytic streptococci and S aureus,
otitis externa, and impetiginized eczema. excluding MRSA. Topical retapamulin 1% ointment is indicated
Selection of a particular antibiotic depends upon the diagnosis for use in adult and pediatric patients, 9 months or older, for the
and, when appropriate, in vitro culture and sensitivity studies treatment of impetigo. Recommended treatment regimen is twice-
of clinical samples. The pathogens isolated from most infected daily application for 5 days. Retapamulin is well tolerated with
dermatoses are group A β-hemolytic streptococci, Staphylococcus only occasional local irritation of the treatment site. Although
aureus, or both. The pathogens present in surgical wounds will uncommon, allergic contact dermatitis has been reported.
be those resident in the environment. Information about regional
patterns of drug resistance is therefore important in selecting a POLYMYXIN B SULFATE
therapeutic agent. Prepackaged topical antibacterial preparations
that contain multiple antibiotics are available in fixed dosages Polymyxin B is a peptide antibiotic effective against Gram-negative
well above the therapeutic threshold. These formulations offer the organisms, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli,
advantages of efficacy in mixed infections, broader coverage for Enterobacter, and Klebsiella. Most strains of Proteus and Serratia