Page 1111 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1111
CHAPTER 62 Drugs Used in the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases 1097
Drugs Used in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and
To CNS
Antiemetic Agents. Other drugs acting on 5-HT receptors are
ENS neuron discussed in Chapters 16, 29, and 30.
ACh, CGRP CHOLINOMIMETIC AGENTS
5HT R Cholinomimetic agonists such as bethanechol stimulate mus-
4
carinic M receptors on muscle cells and at myenteric plexus
3
Submucosal + synapses (see Chapter 7). Bethanechol was used in the past for
IPAN
Dorsal root the treatment of GERD and gastroparesis. Owing to multiple
or cranial Tegaserod cholinergic effects and the advent of less toxic agents, it is now
nerve afferent
seldom used. The acetylcholinesterase inhibitor neostigmine can
enhance gastric, small intestine, and colonic emptying. Intra-
5HT R 5HT R
3 IP venous neostigmine is used for the treatment of hospitalized
5HT
– patients with acute large bowel distention (known as acute colonic
Alosetron pseudo-obstruction or Ogilvie’s syndrome). Administration of
2 mg results in prompt colonic evacuation of flatus and feces
EC
in the majority of patients. Cholinergic effects include excessive
salivation, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and bradycardia.
Gut
lumen
METOCLOPRAMIDE & DOMPERIDONE
Pressure,
other stimuli Metoclopramide and domperidone are dopamine D -receptor
2
antagonists. Within the gastrointestinal tract, activation of dopa-
mine receptors inhibits cholinergic smooth muscle stimulation;
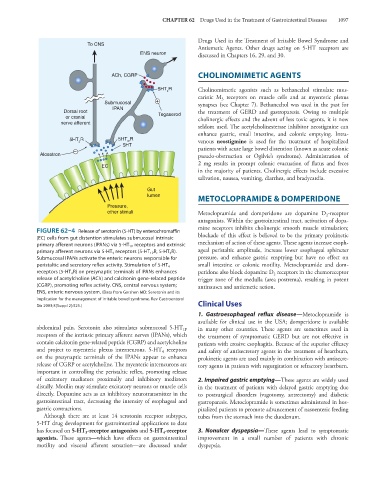
FIGURE 62–4 Release of serotonin (5-HT) by enterochromaffin
(EC) cells from gut distention stimulates submucosal intrinsic blockade of this effect is believed to be the primary prokinetic
primary afferent neurons (IPANs) via 5-HT 1P receptors and extrinsic mechanism of action of these agents. These agents increase esoph-
primary afferent neurons via 5-HT 3 receptors (5-HT 1P R, 5-HT 3 R). ageal peristaltic amplitude, increase lower esophageal sphincter
Submucosal IPANs activate the enteric neurons responsible for pressure, and enhance gastric emptying but have no effect on
peristaltic and secretory reflex activity. Stimulation of 5-HT 4 small intestine or colonic motility. Metoclopramide and dom-
receptors (5-HT 4 R) on presynaptic terminals of IPANs enhances peridone also block dopamine D receptors in the chemoreceptor
2
release of acetylcholine (ACh) and calcitonin gene-related peptide trigger zone of the medulla (area postrema), resulting in potent
(CGRP), promoting reflex activity. CNS, central nervous system; antinausea and antiemetic action.
ENS, enteric nervous system. (Data from Gershon MD: Serotonin and its
implication for the management of irritable bowel syndrome. Rev Gastroenterol
Dis 2003;3[Suppl 2]:S25.) Clinical Uses
1. Gastroesophageal reflux disease—Metoclopramide is
available for clinical use in the USA; domperidone is available
abdominal pain. Serotonin also stimulates submucosal 5-HT in many other countries. These agents are sometimes used in
1P
receptors of the intrinsic primary afferent nerves (IPANs), which the treatment of symptomatic GERD but are not effective in
contain calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and acetylcholine patients with erosive esophagitis. Because of the superior efficacy
and project to myenteric plexus interneurons. 5-HT receptors and safety of antisecretory agents in the treatment of heartburn,
4
on the presynaptic terminals of the IPANs appear to enhance prokinetic agents are used mainly in combination with antisecre-
release of CGRP or acetylcholine. The myenteric interneurons are tory agents in patients with regurgitation or refractory heartburn.
important in controlling the peristaltic reflex, promoting release
of excitatory mediators proximally and inhibitory mediators 2. Impaired gastric emptying—These agents are widely used
distally. Motilin may stimulate excitatory neurons or muscle cells in the treatment of patients with delayed gastric emptying due
directly. Dopamine acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the to postsurgical disorders (vagotomy, antrectomy) and diabetic
gastrointestinal tract, decreasing the intensity of esophageal and gastroparesis. Metoclopramide is sometimes administered in hos-
gastric contractions. pitalized patients to promote advancement of nasoenteric feeding
Although there are at least 14 serotonin receptor subtypes, tubes from the stomach into the duodenum.
5-HT drug development for gastrointestinal applications to date
-receptor antagonists and 5-HT -receptor 3. Nonulcer dyspepsia—These agents lead to symptomatic
has focused on 5-HT 3 4
agonists. These agents—which have effects on gastrointestinal improvement in a small number of patients with chronic
motility and visceral afferent sensation—are discussed under dyspepsia.