Page 1137 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1137
CHAPTER 63 Therapeutic & Toxic Potential of Over-the-Counter Agents 1123
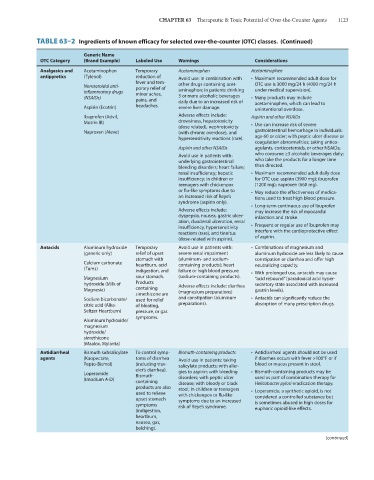
TABLE 63–2 Ingredients of known efficacy for selected over-the-counter (OTC) classes. (Continued)
Generic Name
OTC Category (Brand Example) Labeled Use Warnings Considerations
Analgesics and Acetaminophen Temporary Acetaminophen Acetaminophen
antipyretics (Tylenol) reduction of Avoid use: in combination with • Maximum recommended adult dose for
fever and tem-
Nonsteroidal anti- porary relief of other drugs containing acet- OTC use is 3000 mg/24 h (4000 mg/24 h
inflammatory drugs minor aches, aminophen; in patients drinking under medical supervision).
(NSAIDs) pains, and 3 or more alcoholic beverages • Many products may include
daily due to an increased risk of
Aspirin (Ecotrin) headaches. severe liver damage. acetaminophen, which can lead to
unintentional overdose.
Ibuprofen (Advil, Adverse effects include: Aspirin and other NSAIDs
Motrin IB) drowsiness, hepatotoxicity • Use can increase risk of severe
(dose related), nephrotoxicity
Naproxen (Aleve) (with chronic overdose), and gastrointestinal hemorrhage in individuals:
hypersensitivity reactions (rare). age 60 or older; with peptic ulcer disease or
coagulation abnormalities; taking antico-
Aspirin and other NSAIDs agulants, corticosteroids, or other NSAIDs;
Avoid use in patients with: who consume ≥3 alcoholic beverages daily;
underlying gastrointestinal who take the products for a longer time
bleeding disorders; heart failure; than directed.
renal insufficiency; hepatic • Maximum recommended adult daily dose
insufficiency; in children or for OTC use: aspirin (3900 mg); ibuprofen
teenagers with chickenpox (1200 mg); naproxen (660 mg).
or flu-like symptoms due to • May reduce the effectiveness of medica-
an increased risk of Reye’s tions used to treat high blood pressure.
syndrome (aspirin only).
• Long-term continuous use of ibuprofen
Adverse effects include: may increase the risk of myocardial
dyspepsia, nausea, gastric ulcer- infarction and stroke.
ation, duodenal ulceration, renal
insufficiency, hypersensitivity • Frequent or regular use of ibuprofen may
reactions (rare), and tinnitus interfere with the cardioprotective effect
(dose-related with aspirin). of aspirin.
Antacids Aluminum hydroxide Temporary Avoid use in patients with: • Combinations of magnesium and
(generic only) relief of upset severe renal impairment aluminum hydroxide are less likely to cause
stomach with (aluminum- and sodium- constipation or diarrhea and offer high
Calcium carbonate heartburn, acid containing products); heart neutralizing capacity.
(Tums) indigestion, and failure or high blood pressure • With prolonged use, antacids may cause
Magnesium sour stomach. (sodium-containing products). “acid rebound” (paradoxical acid hyper-
hydroxide (Milk of Products Adverse effects include: diarrhea secretory state associated with increased
Magnesia) containing (magnesium preparations) gastrin levels).
simethicone are
Sodium bicarbonate/ used for relief and constipation (aluminum • Antacids can significantly reduce the
citric acid (Alka- of bloating, preparations). absorption of many prescription drugs.
Seltzer Heartburn) pressure, or gas
symptoms.
Aluminum hydroxide/
magnesium
hydroxide/
simethicone
(Maalox, Mylanta)
Antidiarrheal Bismuth subsalicylate To control symp- Bismuth-containing products • Antidiarrheal agents should not be used
agents (Kaopectate, toms of diarrhea Avoid use in patients: taking if diarrhea occurs with fever >100°F or if
Pepto-Bismol) (including trav- salicylate products; with aller- blood or mucus present in stool.
eler’s diarrhea).
Loperamide Bismuth- gies to aspirin; with bleeding • Bismuth-containing products may be
(Imodium A-D) containing disorders; with peptic ulcer used as part of combination therapy for
Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy.
disease; with bloody or black
products are also stool; in children or teenagers
used to relieve with chickenpox or flu-like • Loperamide, a synthetic opioid, is not
upset stomach symptoms due to an increased considered a controlled substance but
symptoms risk of Reye’s syndrome. is sometimes abused in high doses for
(indigestion, euphoric opioid-like effects.
heartburn,
nausea, gas,
belching).
(continued)