Page 287 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 287
CHAPTER 15 Diuretic Agents 273
Clinical Pharmacokinetics,
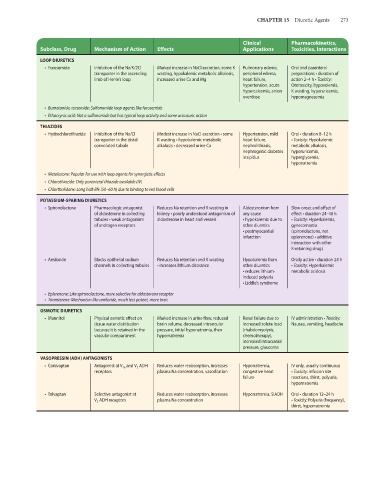
Subclass, Drug Mechanism of Action Effects Applications Toxicities, Interactions
LOOP DIURETICS
• Furosemide Inhibition of the Na/K/2Cl Marked increase in NaCl excretion, some K Pulmonary edema, Oral and parenteral
transporter in the ascending wasting, hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis, peripheral edema, preparations • duration of
limb of Henle’s loop increased urine Ca and Mg heart failure, action 2–4 h • Toxicity:
hypertension, acute Ototoxicity, hypovolemia,
hypercalcemia, anion K wasting, hyperuricemia,
overdose hypomagnesemia
• Bumetanide, torsemide: Sulfonamide loop agents like furosemide
• Ethacrynic acid: Not a sulfonamide but has typical loop activity and some uricosuric action
THIAZIDES
• Hydrochlorothiazide Inhibition of the Na/Cl Modest increase in NaCl excretion • some Hypertension, mild Oral • duration 8–12 h
transporter in the distal K wasting • hypokalemic metabolic heart failure, • Toxicity: Hypokalemic
convoluted tubule alkalosis • decreased urine Ca nephrolithiasis, metabolic alkalosis,
nephrogenic diabetes hyperuricemia,
insipidus hyperglycemia,
hyponatremia
• Metolazone: Popular for use with loop agents for synergistic effects
• Chlorothiazide: Only parenteral thiazide available (IV)
• Chlorthalidone: Long half-life (50–60 h) due to binding to red blood cells
POTASSIUM-SPARING DIURETICS
• Spironolactone Pharmacologic antagonist Reduces Na retention and K wasting in Aldosteronism from Slow onset and offset of
of aldosterone in collecting kidney • poorly understood antagonism of any cause effect • duration 24–48 h
tubules • weak antagonism aldosterone in heart and vessels • hypokalemia due to • Toxicity: Hyperkalemia,
of androgen receptors other diuretics gynecomastia
• postmyocardial (spironolactone, not
infarction eplerenone) • additive
interaction with other
K-retaining drugs
• Amiloride Blocks epithelial sodium Reduces Na retention and K wasting Hypokalemia from Orally active • duration 24 h
channels in collecting tubules • increases lithium clearance other diuretics • Toxicity: Hyperkalemic
• reduces lithium- metabolic acidosis
induced polyuria
• Liddle’s syndrome
• Eplerenone: Like spironolactone, more selective for aldosterone receptor
• Triamterene: Mechanism like amiloride, much less potent, more toxic
OSMOTIC DIURETICS
• Mannitol Physical osmotic effect on Marked increase in urine flow, reduced Renal failure due to IV administration • Toxicity:
tissue water distribution brain volume, decreased intraocular increased solute load Nausea, vomiting, headache
because it is retained in the pressure, initial hyponatremia, then (rhabdomyolysis,
vascular compartment hypernatremia chemotherapy),
increased intracranial
pressure, glaucoma
VASOPRESSIN (ADH) ANTAGONISTS
• Conivaptan Antagonist at V 1a and V 2 ADH Reduces water reabsorption, increases Hyponatremia, IV only, usually continuous
receptors plasma Na concentration, vasodilation congestive heart • Toxicity: Infusion site
failure reactions, thirst, polyuria,
hypernatremia
• Tolvaptan Selective antagonist at Reduces water reabsorption, increases Hyponatremia, SIADH Oral • duration 12–24 h
V 2 ADH receptors plasma Na concentration • Toxicity: Polyuria (frequency),
thirst, hypernatremia