Page 316 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 316
302 SECTION IV Drugs with Important Actions on Smooth Muscle
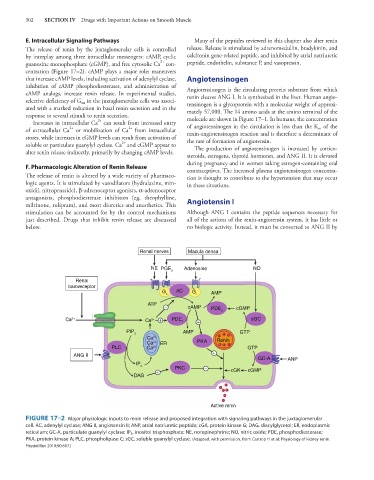
E. Intracellular Signaling Pathways Many of the peptides reviewed in this chapter also alter renin
The release of renin by the juxtaglomerular cells is controlled release. Release is stimulated by adrenomedullin, bradykinin, and
by interplay among three intracellular messengers: cAMP, cyclic calcitonin gene-related peptide, and inhibited by atrial natriuretic
2+
guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), and free cytosolic Ca con- peptide, endothelin, substance P, and vasopressin.
centration (Figure 17–2). cAMP plays a major role; maneuvers
that increase cAMP levels, including activation of adenylyl cyclase, Angiotensinogen
inhibition of cAMP phosphodiesterases, and administration of Angiotensinogen is the circulating protein substrate from which
cAMP analogs, increase renin release. In experimental studies, renin cleaves ANG I. It is synthesized in the liver. Human angio-
selective deficiency of G in the juxtaglomerular cells was associ- tensinogen is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approxi-
sα
ated with a marked reduction in basal renin secretion and in the mately 57,000. The 14 amino acids at the amino terminal of the
response to several stimuli to renin secretion. molecule are shown in Figure 17–1. In humans, the concentration
2+
Increases in intracellular Ca can result from increased entry of angiotensinogen in the circulation is less than the K of the
m
2+
2+
of extracellular Ca or mobilization of Ca from intracellular renin-angiotensinogen reaction and is therefore a determinant of
stores, while increases in cGMP levels can result from activation of the rate of formation of angiotensin.
2+
soluble or particulate guanylyl cyclase. Ca and cGMP appear to The production of angiotensinogen is increased by cortico-
alter renin release indirectly, primarily by changing cAMP levels.
steroids, estrogens, thyroid hormones, and ANG II. It is elevated
during pregnancy and in women taking estrogen-containing oral
F. Pharmacologic Alteration of Renin Release contraceptives. The increased plasma angiotensinogen concentra-
The release of renin is altered by a wide variety of pharmaco- tion is thought to contribute to the hypertension that may occur
logic agents. It is stimulated by vasodilators (hydralazine, min- in these situations.
oxidil, nitroprusside), β-adrenoceptor agonists, α-adrenoceptor
antagonists, phosphodiesterase inhibitors (eg, theophylline, Angiotensin I
milrinone, rolipram), and most diuretics and anesthetics. This
stimulation can be accounted for by the control mechanisms Although ANG I contains the peptide sequences necessary for
just described. Drugs that inhibit renin release are discussed all of the actions of the renin-angiotensin system, it has little or
below. no biologic activity. Instead, it must be converted to ANG II by
Renal nerves Macula densa
NE PGE Adenosine NO
2
Renal
baroreceptor
G AC G AMP
s i
ATP
– cAMP PDE 3 cGMP
Ca 2+ Ca 2+ + PDE 1 + sGC
PIP AMP GTP
2
Ca 2+ Renin
Ca 2+ ER PKA
PLC Ca 2+ GTP
+
ANG II
GC-A ANP
IP
3 PKC –
+ cGK cGMP
DAG
Active renin
FIGURE 17–2 Major physiologic inputs to renin release and proposed integration with signaling pathways in the juxtaglomerular
cell. AC, adenylyl cyclase; ANG II, angiotensin II; ANP, atrial natriuretic peptide; cGK, protein kinase G; DAG, diacylglycerol; ER, endoplasmic
reticulum; GC-A, particulate guanylyl cyclase; IP 3 , inositol trisphosphate; NE, norepinephrine; NO, nitric oxide; PDE, phosphodiesterase;
PKA, protein kinase A; PLC, phospholipase C; sGC, soluble guanylyl cyclase. (Adapted, with permission, from Castrop H et al: Physiology of kidney renin.
Physiol Rev 2010;90:607.)