Page 336 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 336
322 SECTION IV Drugs with Important Actions on Smooth Muscle
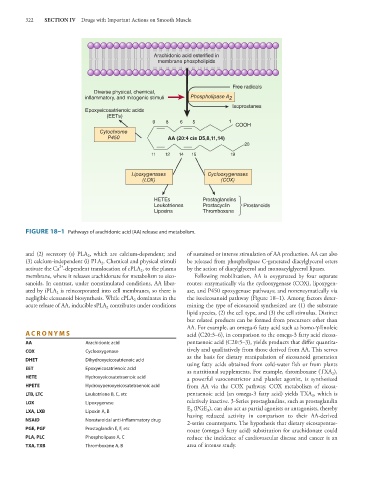
Arachidonic acid esterified in
membrane phospholipids
Free radicals
Diverse physical, chemical,
inflammatory, and mitogenic stimuli Phospholipase A 2
Isoprostanes
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids
(EETs)
9 8 6 5 1
COOH
Cytochrome
P450 AA (20:4 cis D5,8,11,14)
20
11 12 14 15 19
Lipoxygenases Cyclooxygenases
(LOX) (COX)
HETEs Prostaglandins
Leukotrienes Prostacyclin Prostanoids
Lipoxins Thromboxane
FIGURE 18–1 Pathways of arachidonic acid (AA) release and metabolism.
and (2) secretory (s) PLA , which are calcium-dependent; and of sustained or intense stimulation of AA production. AA can also
2
(3) calcium-independent (i) PLA . Chemical and physical stimuli be released from phospholipase C-generated diacylglycerol esters
2
2+
activate the Ca -dependent translocation of cPLA , to the plasma by the action of diacylglycerol and monoacylglycerol lipases.
2
membrane, where it releases arachidonate for metabolism to eico- Following mobilization, AA is oxygenated by four separate
sanoids. In contrast, under nonstimulated conditions, AA liber- routes: enzymatically via the cyclooxygenase (COX), lipoxygen-
ated by iPLA is reincorporated into cell membranes, so there is ase, and P450 epoxygenase pathways; and nonenzymatically via
2
negligible eicosanoid biosynthesis. While cPLA dominates in the the isoeicosanoid pathway (Figure 18–1). Among factors deter-
2
acute release of AA, inducible sPLA contributes under conditions mining the type of eicosanoid synthesized are (1) the substrate
2
lipid species, (2) the cell type, and (3) the cell stimulus. Distinct
but related products can be formed from precursors other than
AA. For example, an omega-6 fatty acid such as homo-γ-linoleic
A CR ON Y MS acid (C20:3–6), in comparison to the omega-3 fatty acid eicosa-
AA Arachidonic acid pentaenoic acid (C20:5–3), yields products that differ quantita-
COX Cyclooxygenase tively and qualitatively from those derived from AA. This serves
as the basis for dietary manipulation of eicosanoid generation
DHET Dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid
using fatty acids obtained from cold-water fish or from plants
EET Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid
as nutritional supplements. For example, thromboxane (TXA ),
2
HETE Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid a powerful vasoconstrictor and platelet agonist, is synthesized
HPETE Hydroxyperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid from AA via the COX pathway. COX metabolism of eicosa-
LTB, LTC Leukotriene B, C, etc pentaenoic acid (an omega-3 fatty acid) yields TXA , which is
3
LOX Lipoxygenase relatively inactive. 3-Series prostaglandins, such as prostaglandin
E (PGE ), can also act as partial agonists or antagonists, thereby
LXA, LXB Lipoxin A, B 3 3
having reduced activity in comparison to their AA-derived
NSAID Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
2-series counterparts. The hypothesis that dietary eicosapentae-
PGE, PGF Prostaglandin E, F, etc noate (omega-3 fatty acid) substitution for arachidonate could
PLA, PLC Phospholipase A, C reduce the incidence of cardiovascular disease and cancer is an
TXA, TXB Thromboxane A, B area of intense study.