Page 339 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 339
CHAPTER 18 The Eicosanoids: Prostaglandins, Thromboxanes, Leukotrienes, & Related Compounds 325
COOH
Arachidonic acid CYP2C, 2J COOH
FLAP 5-LOX O
CYP3A, 4A, 4F
11,12-EET*
OOH
COOH COOH
CH OH
2
20-HETE*
5(S)-HPETE
5-LOX
O
COOH
LTC synthase LTA 4 hydrolase
4
LTA OH OH
OH 4 COOH
COOH
C H S − Cys − Gly LTB 4
5 11
LTC 4 Glu
γ-GT
γ-GL
OH
COOH
Cysteinyl
leukotrienes C 5 11
H
(CysLTs) S − Cys − Gly OH
COOH
LTD 4 Dipeptidase
H
C 5 11 S − Cys
LTE 4
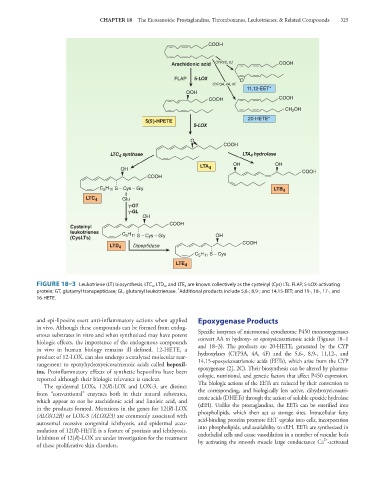
FIGURE 18–3 Leukotriene (LT) biosynthesis. LTC 4 , LTD 4 , and LTE 4 are known collectively as the cysteinyl (Cys) LTs. FLAP, 5-LOX-activating
*
protein; GT, glutamyl transpeptidase; GL, glutamyl leukotrienase. Additional products include 5,6-; 8,9-; and 14,15-EET; and 19-, 18-, 17-, and
16-HETE.
and epi-lipoxins exert anti-inflammatory actions when applied Epoxygenase Products
in vivo. Although these compounds can be formed from endog-
enous substrates in vitro and when synthesized may have potent Specific isozymes of microsomal cytochrome P450 monooxygenases
biologic effects, the importance of the endogenous compounds convert AA to hydroxy- or epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (Figures 18–1
in vivo in human biology remains ill defined. 12-HETE, a and 18–3). The products are 20-HETE, generated by the CYP
product of 12-LOX, can also undergo a catalyzed molecular rear- hydroxylases (CYP3A, 4A, 4F) and the 5,6-, 8,9-, 11,12-, and
rangement to epoxyhydroxyeicosatrienoic acids called hepoxil- 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), which arise from the CYP
ins. Proinflammatory effects of synthetic hepoxilins have been epoxygenase (2J, 2C). Their biosynthesis can be altered by pharma-
reported although their biologic relevance is unclear. cologic, nutritional, and genetic factors that affect P450 expression.
The epidermal LOXs, 12(R)-LOX and LOX-3, are distinct The biologic actions of the EETs are reduced by their conversion to
from “conventional” enzymes both in their natural substrates, the corresponding, and biologically less active, dihydroxyeicosatri-
which appear to not be arachidonic acid and linoleic acid, and enoic acids (DHETs) through the action of soluble epoxide hydrolase
in the products formed. Mutations in the genes for 12(R)-LOX (sEH). Unlike the prostaglandins, the EETs can be esterified into
(ALOX12B) or LOX-3 (ALOXE3) are commonly associated with phospholipids, which then act as storage sites. Intracellular fatty
autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis, and epidermal accu- acid-binding proteins promote EET uptake into cells, incorporation
mulation of 12(R)-HETE is a feature of psoriasis and ichthyosis. into phospholipids, and availability to sEH. EETs are synthesized in
Inhibitors of 12(R)-LOX are under investigation for the treatment endothelial cells and cause vasodilation in a number of vascular beds
2+
of these proliferative skin disorders. by activating the smooth muscle large conductance Ca -activated