Page 391 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 391
CHAPTER 21 Introduction to the Pharmacology of CNS Drugs 377
TABLE 21–2 Summary of neurotransmitter pharmacology in the central nervous system. (Continued)
Receptor Subtypes
Transmitter Anatomy and Preferred Agonists Receptor Antagonists Mechanisms
2+
Opioid peptides Cell bodies at all levels; Mu: bendorphin Naloxone Inhibitory (presynaptic): ↓ Ca
long and short connections conductance, ↓ cAMP
+
Delta: enkephalin Naloxone Inhibitory (postsynaptic): ↑ K
conductance, ↓ cAMP
+
Kappa: dynorphin, Naloxone Inhibitory (postsynaptic): ↑ K
salvinorin A conductance, ↓ cAMP
Orexins Cell bodies in hypothala- OX 1 : orexin A Suvorexant Excitatory, glutamate co-release
mus; project widely
OX 2 : orexins A and B Suvorexant
+
Tachykinins Primary sensory neurons, NK1: substance P Aprepitant Excitatory: ↓ K conductance,
cell bodies at all levels; long methylester ↑ IP 3 , DAG
and short connections
+
NK2: neurokinin A Saredutant Excitatory: ↓ K conductance,
↑ IP 3 , DAG
+
NK3: neurokinin B Osanetant Excitatory: ↓ K conductance,
↑ IP 3 , DAG
2+
Endocannabinoids Widely distributed CB1: anandamide, Rimonabant Inhibitory (presynaptic): ↓ Ca
2-arachidonyglycerol conductance, ↓ cAMP
Note: Many other central transmitters have been identified (see text).
ACET, (S)-1-(2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)-3-(2-carboxy-5-phenylthiophene-3-yl-methyl)-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4-dione; ACPD, trans-1-amino-cyclopentyl-1,3-dicarboxylate; AMPA,
DL-α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; IP 3 , inositol trisphosphate; LSD, lysergic acid diethylamide;
MCPG, α-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine; NBQX, 2,3-dihydroxy-6-nitro-7-sulfamoylbenzo(f)quinoxaline.
A
Glutamine
Glutaminase
C Glutamate
VGLUT
Glutamine
Glutamine
synthetase
Glutamate
mGluR AMPAR NMDAR
B
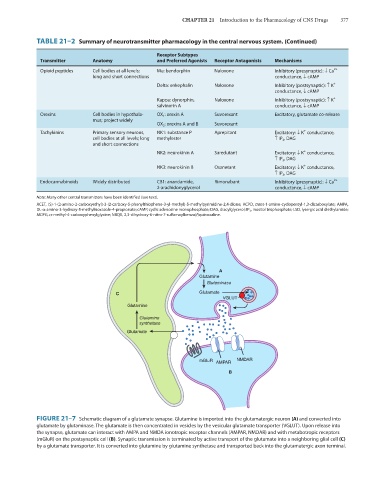
FIGURE 21–7 Schematic diagram of a glutamate synapse. Glutamine is imported into the glutamatergic neuron (A) and converted into
glutamate by glutaminase. The glutamate is then concentrated in vesicles by the vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT). Upon release into
the synapse, glutamate can interact with AMPA and NMDA ionotropic receptor channels (AMPAR, NMDAR) and with metabotropic receptors
(mGluR) on the postsynaptic cell (B). Synaptic transmission is terminated by active transport of the glutamate into a neighboring glial cell (C)
by a glutamate transporter. It is converted into glutamine by glutamine synthetase and transported back into the glutamatergic axon terminal.