Page 388 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 388
374 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
whose cell bodies are located in small discrete nuclei, often in neurons within the hierarchical systems. In the neocortex, these
the brain stem. For example, noradrenergic cell bodies are found fibers have a tangential organization and therefore can influence
primarily in a compact cell group called the locus coeruleus large areas of cortex. In addition, most neurotransmitters utilized
located in the caudal pontine central gray matter and number only by diffuse neuronal systems, including norepinephrine, act pre-
approximately 12,000 neurons on each side of the human brain. dominantly on metabotropic receptors and therefore initiate long-
However, from these limited nuclei, these neurons project widely lasting synaptic effects. Based on these observations, it is clear that
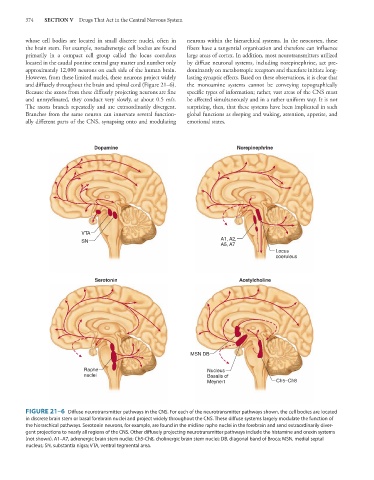
and diffusely throughout the brain and spinal cord (Figure 21–6). the monoamine systems cannot be conveying topographically
Because the axons from these diffusely projecting neurons are fine specific types of information; rather, vast areas of the CNS must
and unmyelinated, they conduct very slowly, at about 0.5 m/s. be affected simultaneously and in a rather uniform way. It is not
The axons branch repeatedly and are extraordinarily divergent. surprising, then, that these systems have been implicated in such
Branches from the same neuron can innervate several function- global functions as sleeping and waking, attention, appetite, and
ally different parts of the CNS, synapsing onto and modulating emotional states.
Dopamine Norepinephrine
VTA
SN A1, A2,
A5, A7
Locus
coeruleus
Serotonin Acetylcholine
MSN DB
Raphe Nucleus
nuclei Basalis of
Meynert Ch5–Ch8
FIGURE 21–6 Diffuse neurotransmitter pathways in the CNS. For each of the neurotransmitter pathways shown, the cell bodies are located
in discrete brain stem or basal forebrain nuclei and project widely throughout the CNS. These diffuse systems largely modulate the function of
the hierarchical pathways. Serotonin neurons, for example, are found in the midline raphe nuclei in the forebrain and send extraordinarily diver-
gent projections to nearly all regions of the CNS. Other diffusely projecting neurotransmitter pathways include the histamine and orexin systems
(not shown). A1–A7, adrenergic brain stem nuclei; Ch5-Ch8, cholinergic brain stem nuclei; DB, diagonal band of Broca; MSN, medial septal
nucleus; SN, substantia nigra; VTA, ventral tegmental area.