Page 426 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 426
412 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
A
Presynaptic terminal Phenytoin, carbamazepine,
of glutamate neuron lamotrigine, lacosamide,
– zonisamide, oxcarbazepine
Na + Voltage-gated
Retigabine K + Na channel
+
Gabapentin,
pregabalin KCNQ K +
channel
– SV2A
– Levetiracetam
2 subunit
of P/Q-type
2+
Ca channel
Glutamate
Felbamate Perampanel
Retigabine K + – –
Postsynaptic KCNQ K + NMDA AMPA
neuron channel receptor receptor
2+
+
+
Na , Ca 2+ Na , (Ca )
B
Presynaptic terminal
of GABA neuron
Astrocyte
Glutamate
Vigabatrin GAD
–
–
GABA
Synaptic
Succinic GABA-T Succinic
semi- GABA semi- GABA-T GABA vesicles
aldehyde aldehyde
– Tiagabine –
GAT-1 GABA
Phenobarbital
Benzodiazepines +
+
Postsynaptic Extrasynaptic Synaptic
neuron GABA receptor GABA receptor
A
A
Cl− Cl−
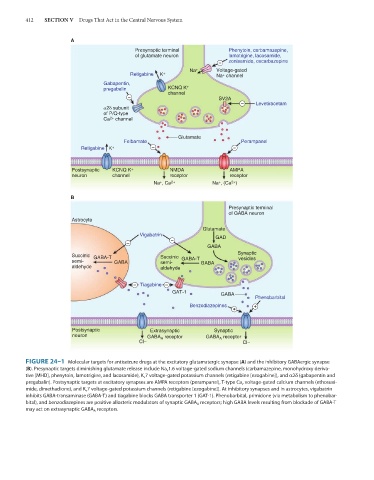
FIGURE 24–1 Molecular targets for antiseizure drugs at the excitatory glutamatergic synapse (A) and the inhibitory GABAergic synapse
(B). Presynaptic targets diminishing glutamate release include Na v 1.6 voltage-gated sodium channels (carbamazepine, monohydroxy deriva-
tive [MHD], phenytoin, lamotrigine, and lacosamide), K v 7 voltage-gated potassium channels (retigabine [ezogabine]), and α2δ (gabapentin and
pregabalin). Postsynaptic targets at excitatory synapses are AMPA receptors (perampanel), T-type Ca v voltage-gated calcium channels (ethosuxi-
mide, dimethadione), and K v 7 voltage-gated potassium channels (retigabine [ezogabine]). At inhibitory synapses and in astrocytes, vigabatrin
inhibits GABA-transaminase (GABA-T) and tiagabine blocks GABA transporter 1 (GAT-1). Phenobarbital, primidone (via metabolism to phenobar-
bital), and benzodiazepines are positive allosteric modulators of synaptic GABA A receptors; high GABA levels resulting from blockade of GABA-T
may act on extrasynaptic GABA A receptors.