Page 450 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 450
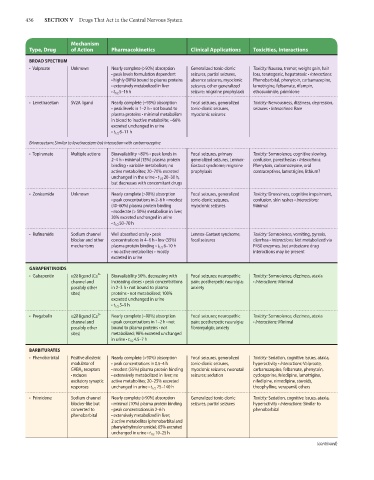
436 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
Mechanism
Type, Drug of Action Pharmacokinetics Clinical Applications Toxicities, Interactions
BROAD SPECTRUM
• Valproate Unknown Nearly complete (>90%) absorption Generalized tonic-clonic Toxicity: Nausea, tremor, weight gain, hair
• peak levels formulation dependent seizures, partial seizures, loss, teratogenic, hepatotoxic • Interactions:
• highly (90%) bound to plasma proteins absence seizures, myoclonic Phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine,
• extensively metabolized in liver seizures, other generalized lamotrigine, felbamate, rifampin,
• t 1/2 5–16 h seizure; migraine prophylaxis ethosuximide, primidone
• Levetiracetam SV2A ligand Nearly complete (~95%) absorption Focal seizures, generalized Toxicity: Nervousness, dizziness, depression,
• peak levels in 1–2 h • not bound to tonic-clonic seizures, seizures • Interactions: Rare
plasma proteins • minimal metabolism myoclonic seizures
in blood to inactive metabolite; ~66%
excreted unchanged in urine
• t 1/2 6–11 h
Brivaracetam: Similar to levetiracetam but interaction with carbamazepine
• Topiramate Multiple actions Bioavailability ~80% • peak levels in Focal seizures, primary Toxicity: Somnolence, cognitive slowing,
2–4 h • minimal (15%) plasma protein generalized seizures, Lennox- confusion, paresthesias • Interactions:
binding • variable metabolism; no Gastaut syndrome; migraine Phenytoin, carbamazepine, oral
active metabolites; 20–70% excreted prophylaxis contraceptives, lamotrigine, lithium?
unchanged in the urine • t 1/2 20–30 h,
but decreases with concomitant drugs
• Zonisamide Unknown Nearly complete (>90%) absorption Focal seizures, generalized Toxicity: Drowsiness, cognitive impairment,
• peak concentrations in 2–6 h • modest tonic-clonic seizures, confusion, skin rashes • Interactions:
(40–60%) plasma protein binding myoclonic seizures Minimal
• moderate (> 50%) metabolism in liver;
30% excreted unchanged in urine
• t 1/2 50–70 h
• Rufinamide Sodium channel Well absorbed orally • peak Lennox-Gastaut syndrome; Toxicity: Somnolence, vomiting, pyrexia,
blocker and other concentrations in 4–6 h • low (35%) focal seizures diarrhea • Interactions: Not metabolized via
mechanisms plasma protein binding • t 1/2 6–10 h P450 enzymes, but antiseizure drug
• no active metabolites • mostly interactions may be present
excreted in urine
GABAPENTINOIDS
2+
• Gabapentin α2δ ligand (Ca Bioavailability 50%, decreasing with Focal seizures; neuropathic Toxicity: Somnolence, dizziness, ataxia
channel and increasing doses • peak concentrations pain; postherpetic neuralgia; • Interactions: Minimal
possibly other in 2–3 h • not bound to plasma anxiety
sites) proteins • not metabolized; 100%
excreted unchanged in urine
• t 1/2 5–9 h
2+
• Pregabalin α2δ ligand (Ca Nearly complete (~90%) absorption Focal seizures; neuropathic Toxicity: Somnolence, dizziness, ataxia
channel and • peak concentrations in 1–2 h • not pain; postherpetic neuralgia; • Interactions: Minimal
possibly other bound to plasma proteins • not fibromyalgia; anxiety
sites) metabolized; 98% excreted unchanged
in urine • t 1/2 4.5–7 h
BARBITURATES
• Phenobarbital Positive allosteric Nearly complete (>90%) absorption Focal seizures, generalized Toxicity: Sedation, cognitive issues, ataxia,
modulator of • peak concentrations in 0.5–4 h tonic-clonic seizures, hyperactivity • Interactions: Valproate,
GABA A receptors • modest (55%) plasma protein binding myoclonic seizures, neonatal carbamazepine, felbamate, phenytoin,
• reduces • extensively metabolized in liver; no seizures; sedation cyclosporine, felodipine, lamotrigine,
excitatory synaptic active metabolites; 20–25% excreted nifedipine, nimodipine, steroids,
responses unchanged in urine • t 1/2 75–140 h theophylline, verapamil, others
• Primidone Sodium channel Nearly complete (>90%) absorption Generalized tonic-clonic Toxicity: Sedation, cognitive issues, ataxia,
blocker-like but • minimal (10%) plasma protein binding seizures, partial seizures hyperactivity • Interactions: Similar to
converted to • peak concentrations in 2–6 h phenobarbital
phenobarbital • extensively metabolized in liver;
2 active metabolites (phenobarbital and
phenylethylmalonamide); 65% excreted
unchanged in urine • t 1/2 10–25 h
(continued)