Page 451 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 451
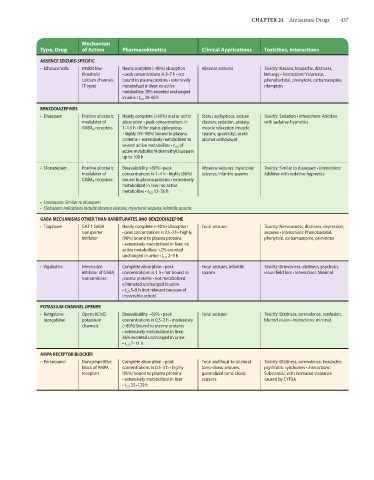
CHAPTER 24 Antiseizure Drugs 437
Mechanism
Type, Drug of Action Pharmacokinetics Clinical Applications Toxicities, Interactions
ABSENCE SEIZURE-SPECIFIC
• Ethosuximide Inhibit low- Nearly complete (>90%) absorption Absence seizures Toxicity: Nausea, headache, dizziness,
threshold • peak concentrations in 3–7 h • not lethargy • Interactions: Valproate,
calcium channels bound to plasma proteins • extensively phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine,
(T-type) metabolized in liver; no active rifampicin
metabolites; 20% excreted unchanged
in urine • t 1/2 20–60 h
BENZODIAZEPINES
• Diazepam Positive allosteric Nearly complete (>90%) oral or rectal Status epilepticus, seizure Toxicity: Sedation • Interactions: Additive
modulator of absorption • peak concentrations in clusters; sedation, anxiety, with sedative-hypnotics
GABA A receptors 1–1.5 h • IV for status epilepticus muscle relaxation (muscle
• highly (95–98%) bound to plasma spasms, spasticity), acute
proteins • extensively metabolized to alcohol withdrawal
several active metabolites • t 1/2 of
active metabolite N-desmethyldiazepam
up to 100 h
• Clonazepam Positive allosteric Bioavailability >80% • peak Absence seizures, myoclonic Toxicity: Similar to diazepam • Interactions:
modulator of concentrations in 1–4 h • highly (86%) seizures, infantile spasms Additive with sedative-hypnotics
GABA A receptors bound to plasma proteins • extensively
metabolized in liver; no active
metabolites • t 1/2 12–56 h
• Lorazepam: Similar to diazepam
• Clobazam: Indications include absence seizures, myoclonic seizures, infantile spasms
GABA MECHANISMS OTHER THAN BARBITURATES AND BENZODIAZEPINE
• Tiagabine GAT-1 GABA Nearly complete (~90%) absorption Focal seizures Toxicity: Nervousness, dizziness, depression,
transporter • peak concentrations in 0.5–2 h • highly seizures • Interactions: Phenobarbital,
inhibitor (96%) bound to plasma proteins phenytoin, carbamazepine, primidone
• extensively metabolized in liver; no
active metabolites; <2% excreted
unchanged in urine • t 1/2 2–9 h
• Vigabatrin Irreversible Complete absorption • peak Focal seizures, infantile Toxicity: Drowsiness, dizziness, psychosis,
inhibitor of GABA concentrations in 1 h • not bound to spasms visual field loss • Interactions: Minimal
transaminase plasma proteins • not metabolized;
eliminated unchanged in urine
• t 1/2 5–8 h (not relevant because of
irreversible action)
POTASSIUM CHANNEL OPENER
• Retigabine Opens KCNQ Bioavailability ~60% • peak Focal seizures Toxicity: Dizziness, somnolence, confusion,
(ezogabine) potassium concentrations in 0.5–2 h • moderately blurred vision • Interactions: minimal
channels (~80%) bound to plasma proteins
• extensively metabolized in liver;
36% excreted unchanged in urine
• t 1/2 7–11 h
AMPA RECEPTOR BLOCKER
• Perampanel Noncompetitive Complete absorption • peak Focal and focal-to-bilateral Toxicity: Dizziness, somnolence, headache;
block of AMPA concentrations in 0.5–3 h • highly tonic-clonic seizures, psychiatric syndromes • Interactions:
receptors (95%) bound to plasma proteins generalized tonic-clonic Substantial, with increased clearance
• extensively metabolized in liver seizures caused by CYP3A
• t 1/2 25–129 h