Page 456 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 456
442 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
A Presynaptic neuron Action
potential
GABA
or Glycine
Anesthetics
GABA A Cl – K + K + K +
Cl – receptor K +
Glycine K + +
receptor K
K + channel
Cl – Cl – +
Cl – Cl – Cl – Cl – Cl – K K +
Cl – Cl –
Postsynaptic neuron
B Presynaptic neuron Action
potential
Glutamate
or ACh
Anesthetics
Na +
Ca 2+ NMDA Mg 2+ Na +
nACh Na + receptor Ca 2+
receptor
Ca 2+
Ca 2+ Mg 2+ Na +
Na
Na + Ca 2+ Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ + Ca 2+
Na + Na + Mg 2+ Na Na +
Ca 2+ Postsynaptic neuron
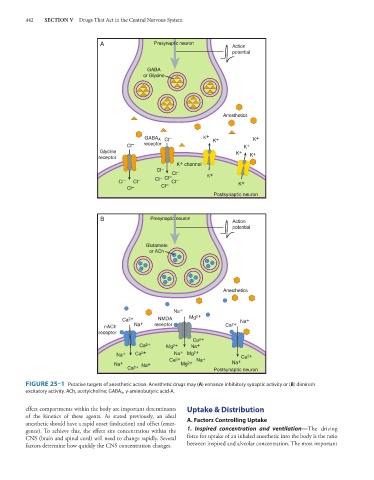
FIGURE 25–1 Putative targets of anesthetic action. Anesthetic drugs may (A) enhance inhibitory synaptic activity or (B) diminish
excitatory activity. ACh, acetylcholine; GABA A , γ-aminobutyric acid-A.
effect compartments within the body are important determinants Uptake & Distribution
of the kinetics of these agents. As stated previously, an ideal A. Factors Controlling Uptake
anesthetic should have a rapid onset (induction) and offset (emer-
gence). To achieve this, the effect site concentration within the 1. Inspired concentration and ventilation—The driving
CNS (brain and spinal cord) will need to change rapidly. Several force for uptake of an inhaled anesthetic into the body is the ratio
factors determine how quickly the CNS concentration changes. between inspired and alveolar concentration. The most important