Page 493 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 493
CHAPTER 27 Skeletal Muscle Relaxants 479
Depolarizing Block
Nondepolarizing
No Drug Block Phase I Phase II
Train-of-four Fade Constant but Fade
diminished
TOF-R = TOF-R = TOF-R = TOF-R =
1.0 0.4 1.0 0.4
Double burst Fade No fade Fade
Posttetanic Present Absent Present
potentiation * PTC =
> 6 PTC = 3 * PTC = 3 *
*
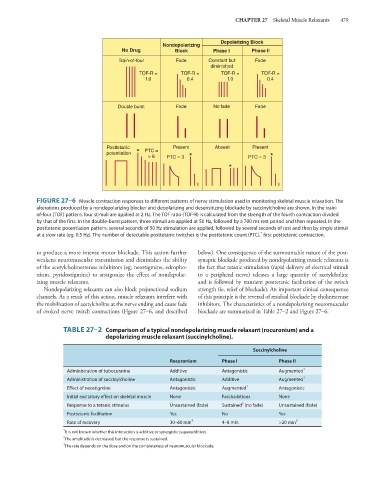
FIGURE 27–6 Muscle contraction responses to different patterns of nerve stimulation used in monitoring skeletal muscle relaxation. The
alterations produced by a nondepolarizing blocker and depolarizing and desensitizing blockade by succinylcholine are shown. In the train-
of-four (TOF) pattern, four stimuli are applied at 2 Hz. The TOF ratio (TOF-R) is calculated from the strength of the fourth contraction divided
by that of the first. In the double-burst pattern, three stimuli are applied at 50 Hz, followed by a 700 ms rest period and then repeated. In the
posttetanic potentiation pattern, several seconds of 50 Hz stimulation are applied, followed by several seconds of rest and then by single stimuli
*
at a slow rate (eg, 0.5 Hz). The number of detectable posttetanic twitches is the posttetanic count (PTC), first posttetanic contraction.
to produce a more intense motor blockade. This action further below). One consequence of the surmountable nature of the post-
weakens neuromuscular transmission and diminishes the ability synaptic blockade produced by nondepolarizing muscle relaxants is
of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (eg, neostigmine, edropho- the fact that tetanic stimulation (rapid delivery of electrical stimuli
nium, pyridostigmine) to antagonize the effect of nondepolar- to a peripheral nerve) releases a large quantity of acetylcholine
izing muscle relaxants. and is followed by transient posttetanic facilitation of the twitch
Nondepolarizing relaxants can also block prejunctional sodium strength (ie, relief of blockade). An important clinical consequence
channels. As a result of this action, muscle relaxants interfere with of this principle is the reversal of residual blockade by cholinesterase
the mobilization of acetylcholine at the nerve ending and cause fade inhibitors. The characteristics of a nondepolarizing neuromuscular
of evoked nerve twitch contractions (Figure 27–6, and described blockade are summarized in Table 27–2 and Figure 27–6.
TABLE 27–2 Comparison of a typical nondepolarizing muscle relaxant (rocuronium) and a
depolarizing muscle relaxant (succinylcholine).
Succinylcholine
Rocuronium Phase I Phase II
Administration of tubocurarine Additive Antagonistic Augmented 1
Administration of succinylcholine Antagonistic Additive Augmented 1
Effect of neostigmine Antagonistic Augmented 1 Antagonistic
Initial excitatory effect on skeletal muscle None Fasciculations None
2
Response to a tetanic stimulus Unsustained (fade) Sustained (no fade) Unsustained (fade)
Posttetanic facilitation Yes No Yes
Rate of recovery 30–60 min 3 4–8 min >20 min 3
1
It is not known whether this interaction is additive or synergistic (superadditive).
2 The amplitude is decreased, but the response is sustained.
3
The rate depends on the dose and on the completeness of neuromuscular blockade.