Page 496 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 496
482 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
Isoflurane
(1.25 MAC)
1 min
2
Tubocurarine (3 mg/m ) 23 min
Halothane
(1.25 MAC)
1 min
2
Tubocurarine (6 mg/m ) 11 min
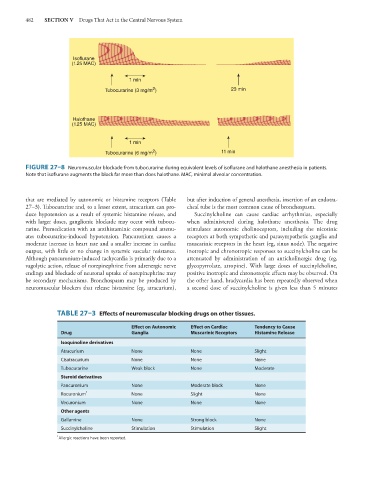
FIGURE 27–8 Neuromuscular blockade from tubocurarine during equivalent levels of isoflurane and halothane anesthesia in patients.
Note that isoflurane augments the block far more than does halothane. MAC, minimal alveolar concentration.
that are mediated by autonomic or histamine receptors (Table but after induction of general anesthesia, insertion of an endotra-
27–3). Tubocurarine and, to a lesser extent, atracurium can pro- cheal tube is the most common cause of bronchospasm.
duce hypotension as a result of systemic histamine release, and Succinylcholine can cause cardiac arrhythmias, especially
with larger doses, ganglionic blockade may occur with tubocu- when administered during halothane anesthesia. The drug
rarine. Premedication with an antihistaminic compound attenu- stimulates autonomic cholinoceptors, including the nicotinic
ates tubocurarine-induced hypotension. Pancuronium causes a receptors at both sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia and
moderate increase in heart rate and a smaller increase in cardiac muscarinic receptors in the heart (eg, sinus node). The negative
output, with little or no change in systemic vascular resistance. inotropic and chronotropic responses to succinylcholine can be
Although pancuronium-induced tachycardia is primarily due to a attenuated by administration of an anticholinergic drug (eg,
vagolytic action, release of norepinephrine from adrenergic nerve glycopyrrolate, atropine). With large doses of succinylcholine,
endings and blockade of neuronal uptake of norepinephrine may positive inotropic and chronotropic effects may be observed. On
be secondary mechanisms. Bronchospasm may be produced by the other hand, bradycardia has been repeatedly observed when
neuromuscular blockers that release histamine (eg, atracurium), a second dose of succinylcholine is given less than 5 minutes
TABLE 27–3 Effects of neuromuscular blocking drugs on other tissues.
Effect on Autonomic Effect on Cardiac Tendency to Cause
Drug Ganglia Muscarinic Receptors Histamine Release
Isoquinoline derivatives
Atracurium None None Slight
Cisatracurium None None None
Tubocurarine Weak block None Moderate
Steroid derivatives
Pancuronium None Moderate block None
Rocuronium 1 None Slight None
Vecuronium None None None
Other agents
Gallamine None Strong block None
Succinylcholine Stimulation Stimulation Slight
1 Allergic reactions have been reported.