Page 529 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 529
CHAPTER 29 Antipsychotic Agents & Lithium 515
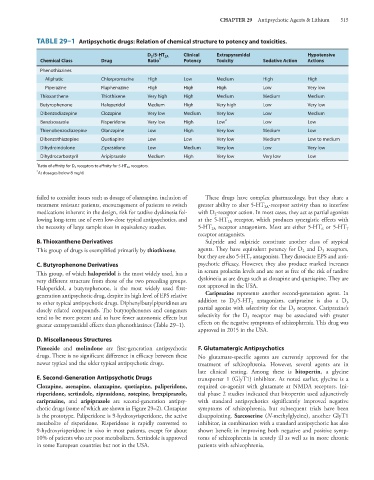
TABLE 29–1 Antipsychotic drugs: Relation of chemical structure to potency and toxicities.
D 2 /5-HT 2A Clinical Extrapyramidal Hypotensive
Chemical Class Drug Ratio 1 Potency Toxicity Sedative Action Actions
Phenothiazines
Aliphatic Chlorpromazine High Low Medium High High
Piperazine Fluphenazine High High High Low Very low
Thioxanthene Thiothixene Very high High Medium Medium Medium
Butyrophenone Haloperidol Medium High Very high Low Very low
Dibenzodiazepine Clozapine Very low Medium Very low Low Medium
Benzisoxazole Risperidone Very low High Low 2 Low Low
Thienobenzodiazepine Olanzapine Low High Very low Medium Low
Dibenzothiazepine Quetiapine Low Low Very low Medium Low to medium
Dihydroindolone Ziprasidone Low Medium Very low Low Very low
Dihydrocarbostyril Aripiprazole Medium High Very low Very low Low
1
Ratio of affinity for D 2 receptors to affinity for 5-HT 2A receptors.
2 At dosages below 8 mg/d.
failed to consider issues such as dosage of olanzapine, inclusion of These drugs have complex pharmacology, but they share a
treatment resistant patients, encouragement of patients to switch greater ability to alter 5-HT -receptor activity than to interfere
2A
medications inherent in the design, risk for tardive dyskinesia fol- with D -receptor action. In most cases, they act as partial agonists
2
lowing long-term use of even low-dose typical antipsychotics, and at the 5-HT receptor, which produces synergistic effects with
1A
the necessity of large sample sizes in equivalency studies. 5-HT receptor antagonism. Most are either 5-HT or 5-HT
7
2A
6
receptor antagonists.
B. Thioxanthene Derivatives Sulpride and sulpiride constitute another class of atypical
This group of drugs is exemplified primarily by thiothixene. agents. They have equivalent potency for D and D receptors,
2
3
but they are also 5-HT antagonists. They dissociate EPS and anti-
7
C. Butyrophenone Derivatives psychotic efficacy. However, they also produce marked increases
This group, of which haloperidol is the most widely used, has a in serum prolactin levels and are not as free of the risk of tardive
very different structure from those of the two preceding groups. dyskinesia as are drugs such as clozapine and quetiapine. They are
Haloperidol, a butyrophenone, is the most widely used first- not approved in the USA.
generation antipsychotic drug, despite its high level of EPS relative Cariprazine represents another second-generation agent. In
to other typical antipsychotic drugs. Diphenylbutylpiperidines are addition to D /5-HT antagonism, cariprazine is also a D
2
2
3
closely related compounds. The butyrophenones and congeners partial agonist with selectivity for the D receptor. Cariprazine’s
3
tend to be more potent and to have fewer autonomic effects but selectivity for the D receptor may be associated with greater
3
greater extrapyramidal effects than phenothiazines (Table 29–1). effects on the negative symptoms of schizophrenia. This drug was
approved in 2015 in the USA.
D. Miscellaneous Structures
Pimozide and molindone are first-generation antipsychotic F. Glutamatergic Antipsychotics
drugs. There is no significant difference in efficacy between these No glutamate-specific agents are currently approved for the
newer typical and the older typical antipsychotic drugs. treatment of schizophrenia. However, several agents are in
late clinical testing. Among these is bitopertin, a glycine
E. Second-Generation Antipsychotic Drugs transporter 1 (GlyT1) inhibitor. As noted earlier, glycine is a
Clozapine, asenapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, paliperidone, required co-agonist with glutamate at NMDA receptors. Ini-
risperidone, sertindole, ziprasidone, zotepine, brexpiprazole, tial phase 2 studies indicated that bitopertin used adjunctively
cariprazine, and aripiprazole are second-generation antipsy- with standard antipsychotics significantly improved negative
chotic drugs (some of which are shown in Figure 29–2). Clozapine symptoms of schizophrenia, but subsequent trials have been
is the prototype. Paliperidone is 9-hydroxyrisperidone, the active disappointing. Sarcoserine (N-methylglycine), another GlyT1
metabolite of risperidone. Risperidone is rapidly converted to inhibitor, in combination with a standard antipsychotic has also
9-hydroxyrisperidone in vivo in most patients, except for about shown benefit in improving both negative and positive symp-
10% of patients who are poor metabolizers. Sertindole is approved toms of schizophrenia in acutely ill as well as in more chronic
in some European countries but not in the USA. patients with schizophrenia.