Page 534 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 534
520 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
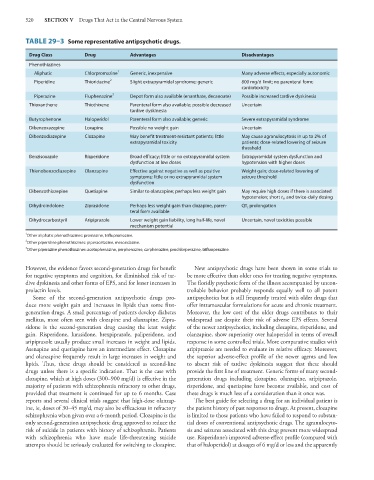
TABLE 29–3 Some representative antipsychotic drugs.
Drug Class Drug Advantages Disadvantages
Phenothiazines
Aliphatic Chlorpromazine 1 Generic, inexpensive Many adverse effects, especially autonomic
Piperidine Thioridazine 2 Slight extrapyramidal syndrome; generic 800 mg/d limit; no parenteral form;
cardiotoxicity
Piperazine Fluphenazine 3 Depot form also available (enanthate, decanoate) Possible increased tardive dyskinesia
Thioxanthene Thiothixene Parenteral form also available; possible decreased Uncertain
tardive dyskinesia
Butyrophenone Haloperidol Parenteral form also available; generic Severe extrapyramidal syndrome
Dibenzoxazepine Loxapine Possible no weight gain Uncertain
Dibenzodiazepine Clozapine May benefit treatment-resistant patients; little May cause agranulocytosis in up to 2% of
extrapyramidal toxicity patients; dose-related lowering of seizure
threshold
Benzisoxazole Risperidone Broad efficacy; little or no extrapyramidal system Extrapyramidal system dysfunction and
dysfunction at low doses hypotension with higher doses
Thienobenzodiazepine Olanzapine Effective against negative as well as positive Weight gain; dose-related lowering of
symptoms; little or no extrapyramidal system seizure threshold
dysfunction
Dibenzothiazepine Quetiapine Similar to olanzapine; perhaps less weight gain May require high doses if there is associated
hypotension; short t ½ and twice-daily dosing
Dihydroindolone Ziprasidone Perhaps less weight gain than clozapine, paren- QT c prolongation
teral form available
Dihydrocarbostyril Aripiprazole Lower weight gain liability, long half-life, novel Uncertain, novel toxicities possible
mechanism potential
1 Other aliphatic phenothiazines: promazine, triflupromazine.
2
Other piperidine phenothiazines: piperacetazine, mesoridazine.
3 Other piperazine phenothiazines: acetophenazine, perphenazine, carphenazine, prochlorperazine, trifluoperazine.
However, the evidence favors second-generation drugs for benefit New antipsychotic drugs have been shown in some trials to
for negative symptoms and cognition, for diminished risk of tar- be more effective than older ones for treating negative symptoms.
dive dyskinesia and other forms of EPS, and for lesser increases in The floridly psychotic form of the illness accompanied by uncon-
prolactin levels. trollable behavior probably responds equally well to all potent
Some of the second-generation antipsychotic drugs pro- antipsychotics but is still frequently treated with older drugs that
duce more weight gain and increases in lipids than some first- offer intramuscular formulations for acute and chronic treatment.
generation drugs. A small percentage of patients develop diabetes Moreover, the low cost of the older drugs contributes to their
mellitus, most often seen with clozapine and olanzapine. Zipra- widespread use despite their risk of adverse EPS effects. Several
sidone is the second-generation drug causing the least weight of the newer antipsychotics, including clozapine, risperidone, and
gain. Risperidone, lurasidone, brexpiprazole, paliperidone, and olanzapine, show superiority over haloperidol in terms of overall
aripiprazole usually produce small increases in weight and lipids. response in some controlled trials. More comparative studies with
Asenapine and quetiapine have an intermediate effect. Clozapine aripiprazole are needed to evaluate its relative efficacy. Moreover,
and olanzapine frequently result in large increases in weight and the superior adverse-effect profile of the newer agents and low
lipids. Thus, these drugs should be considered as second-line to absent risk of tardive dyskinesia suggest that these should
drugs unless there is a specific indication. That is the case with provide the first line of treatment. Generic forms of many second-
clozapine, which at high doses (300–900 mg/d) is effective in the generation drugs including clozapine, olanzapine, aripiprazole,
majority of patients with schizophrenia refractory to other drugs, risperidone, and quetiapine have become available, and cost of
provided that treatment is continued for up to 6 months. Case these drugs is much less of a consideration than it once was.
reports and several clinical trials suggest that high-dose olanzap- The best guide for selecting a drug for an individual patient is
ine, ie, doses of 30–45 mg/d, may also be efficacious in refractory the patient history of past responses to drugs. At present, clozapine
schizophrenia when given over a 6-month period. Clozapine is the is limited to those patients who have failed to respond to substan-
only second-generation antipsychotic drug approved to reduce the tial doses of conventional antipsychotic drugs. The agranulocyto-
risk of suicide in patients with history of schizophrenia. Patients sis and seizures associated with this drug prevent more widespread
with schizophrenia who have made life-threatening suicide use. Risperidone’s improved adverse-effect profile (compared with
attempts should be seriously evaluated for switching to clozapine. that of haloperidol) at dosages of 6 mg/d or less and the apparently