Page 556 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 556
542 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
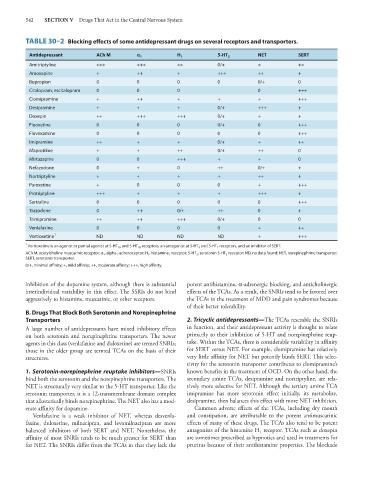
TABLE 30–2 Blocking effects of some antidepressant drugs on several receptors and transporters.
Antidepressant ACh M ` 1 H 1 5-HT 2 NET SERT
Amitriptyline +++ +++ ++ 0/+ + ++
Amoxapine + ++ + +++ ++ +
Bupropion 0 0 0 0 0/+ 0
Citalopram, escitalopram 0 0 0 0 +++
Clomipramine + ++ + + + +++
Desipramine + + + 0/+ +++ +
Doxepin ++ +++ +++ 0/+ + +
Fluoxetine 0 0 0 0/+ 0 +++
Fluvoxamine 0 0 0 0 0 +++
Imipramine ++ + + 0/+ + ++
Maprotiline + + ++ 0/+ ++ 0
Mirtazapine 0 0 +++ + + 0
Nefazodone 0 + 0 ++ 0/+ +
Nortriptyline + + + + ++ +
Paroxetine + 0 0 0 + +++
Protriptyline +++ + + + +++ +
Sertraline 0 0 0 0 0 +++
Trazodone 0 ++ 0/+ ++ 0 +
Trimipramine ++ ++ +++ 0/+ 0 0
Venlafaxine 0 0 0 0 + ++
Vortioxetine 1 ND ND ND ND + +++
1 Vortioxetine is an agonist or partial agonist at 5-HT 1A and 5-HT 1B receptors, an antagonist at 5-HT 3 and 5-HT 7 receptors, and an inhibitor of SERT.
ACh M, acetylcholine muscarinic receptor; α 1 , alpha 1 -adrenoceptor; H 1 , histamine 1 receptor; 5-HT 2 , serotonin 5-HT 2 receptor; ND, no data found; NET, norepinephrine transporter;
SERT, serotonin transporter.
0/+, minimal affinity; +, mild affinity; ++, moderate affinity; +++, high affinity.
inhibition of the dopamine system, although there is substantial potent antihistamine, α-adrenergic blocking, and anticholinergic
interindividual variability in this effect. The SSRIs do not bind effects of the TCAs. As a result, the SNRIs tend to be favored over
aggressively to histamine, muscarinic, or other receptors. the TCAs in the treatment of MDD and pain syndromes because
of their better tolerability.
B. Drugs That Block Both Serotonin and Norepinephrine
Transporters 2. Tricyclic antidepressants—The TCAs resemble the SNRIs
A large number of antidepressants have mixed inhibitory effects in function, and their antidepressant activity is thought to relate
on both serotonin and norepinephrine transporters. The newer primarily to their inhibition of 5-HT and norepinephrine reup-
agents in this class (venlafaxine and duloxetine) are termed SNRIs; take. Within the TCAs, there is considerable variability in affinity
those in the older group are termed TCAs on the basis of their for SERT versus NET. For example, clomipramine has relatively
structures. very little affinity for NET but potently binds SERT. This selec-
tivity for the serotonin transporter contributes to clomipramine’s
1. Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors—SNRIs known benefits in the treatment of OCD. On the other hand, the
bind both the serotonin and the norepinephrine transporters. The secondary amine TCAs, desipramine and nortriptyline, are rela-
NET is structurally very similar to the 5-HT transporter. Like the tively more selective for NET. Although the tertiary amine TCA
serotonin transporter, it is a 12-transmembrane domain complex imipramine has more serotonin effect initially, its metabolite,
that allosterically binds norepinephrine. The NET also has a mod- desipramine, then balances this effect with more NET inhibition.
erate affinity for dopamine. Common adverse effects of the TCAs, including dry mouth
Venlafaxine is a weak inhibitor of NET, whereas desvenla- and constipation, are attributable to the potent antimuscarinic
faxine, duloxetine, milnacipran, and levomilnacipran are more effects of many of these drugs. The TCAs also tend to be potent
balanced inhibitors of both SERT and NET. Nonetheless, the antagonists of the histamine H 1 receptor. TCAs such as doxepin
affinity of most SNRIs tends to be much greater for SERT than are sometimes prescribed as hypnotics and used in treatments for
for NET. The SNRIs differ from the TCAs in that they lack the pruritus because of their antihistamine properties. The blockade