Page 552 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 552
538 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
O
N R 2 C C
R 1 R 1 R 1
R :–(CH ) N(CH ) R : = CH(CH ) N(CH ) R : = CH(CH ) N(CH )
3 2
1
1
2 3
2 2
3 2
1
2 2
3 2
R : H
2
Imipramine Amitriptyline Doxepin
R : = (CH ) NHCH 3 R : = CH(CH ) NHCH 3
2 2
1
1
2 3
R 2 : H Nortriptyline
Desipramine
R 1
R : = (CH ) N(CH ) : = (CH ) NCH
2 3
3 2
1
2 3
R : – Cl R 1 Protriptyline 3
2
Clomipramine
R : = CH CH(CH) CH N(CH )
2
3
2
1
3 2
R : – H
2
Trimipramine
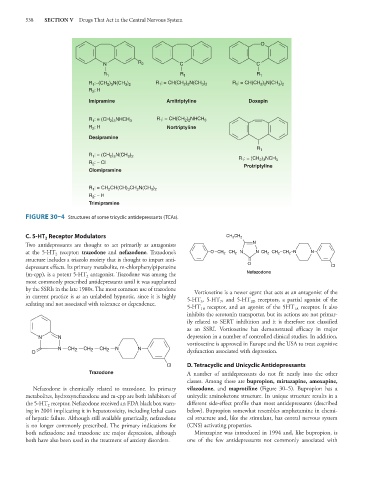
FIGURE 30–4 Structures of some tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs).
C. 5-HT Receptor Modulators CH 3 CH 2
2
Two antidepressants are thought to act primarily as antagonists N
at the 5-HT receptor: trazodone and nefazodone. Trazodone’s O CH 2 CH 2 N N CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 N N
2
structure includes a triazolo moiety that is thought to impart anti-
depressant effects. Its primary metabolite, m-chlorphenylpiperazine O CI
(m-cpp), is a potent 5-HT antagonist. Trazodone was among the Nefazodone
2
most commonly prescribed antidepressants until it was supplanted
by the SSRIs in the late 1980s. The most common use of trazodone Vortioxetine is a newer agent that acts as an antagonist of the
in current practice is as an unlabeled hypnotic, since it is highly 5-HT , 5-HT , and 5-HT receptors, a partial agonist of the
sedating and not associated with tolerance or dependence. 3 7 1D
5-HT receptor, and an agonist of the 5HT receptor. It also
1A
1B
inhibits the serotonin transporter, but its actions are not primar-
ily related to SERT inhibition and it is therefore not classified
as an SSRI. Vortioxetine has demonstrated efficacy in major
N N depression in a number of controlled clinical studies. In addition,
vortioxetine is approved in Europe and the USA to treat cognitive
N CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 N N
O dysfunction associated with depression.
Cl D. Tetracyclic and Unicyclic Antidepressants
Trazodone A number of antidepressants do not fit neatly into the other
classes. Among these are bupropion, mirtazapine, amoxapine,
Nefazodone is chemically related to trazodone. Its primary vilazodone, and maprotiline (Figure 30–5). Bupropion has a
metabolites, hydroxynefazodone and m-cpp are both inhibitors of unicyclic aminoketone structure. Its unique structure results in a
the 5-HT receptor. Nefazodone received an FDA black box warn- different side-effect profile than most antidepressants (described
2
ing in 2001 implicating it in hepatotoxicity, including lethal cases below). Bupropion somewhat resembles amphetamine in chemi-
of hepatic failure. Although still available generically, nefazodone cal structure and, like the stimulant, has central nervous system
is no longer commonly prescribed. The primary indications for (CNS) activating properties.
both nefazodone and trazodone are major depression, although Mirtazapine was introduced in 1994 and, like bupropion, is
both have also been used in the treatment of anxiety disorders. one of the few antidepressants not commonly associated with