Page 549 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 549
CHAPTER 30 Antidepressant Agents 535
Serotonergic Noradrenergic
Tryptophan Tyrosine
Tryptophan Tyrosine
hydroxylase hydroxylase
Serotonin Norepinephrine
Presynaptic
axon
MAO-A
β γ
α
5-HT 1B Metabolites
Serotonin γ β
receptors
α
α 2
Adrenoceptor
5-HT 1A
α β γ
SERT NET
S
α
β γ α Postsynaptic
G β γ neuron
i PLC
G s
AC
IP , DAG cAMP
3
ATP
PKC PKA
Cytoplasm
CREB
Nucleus
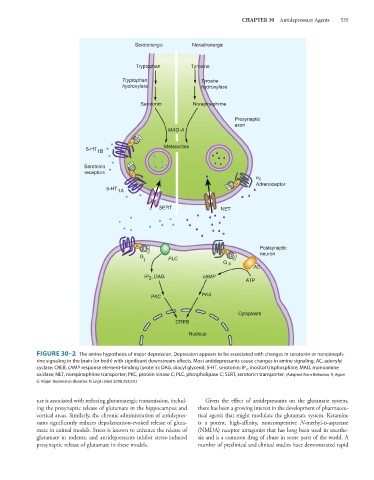
FIGURE 30–2 The amine hypothesis of major depression. Depression appears to be associated with changes in serotonin or norepineph-
rine signaling in the brain (or both) with significant downstream effects. Most antidepressants cause changes in amine signaling. AC, adenylyl
cyclase; CREB, cAMP response element-binding (protein); DAG, diacyl glycerol; 5-HT, serotonin; IP 3 , inositol trisphosphate; MAO, monoamine
oxidase; NET, norepinephrine transporter; PKC, protein kinase C; PLC, phospholipase C; SERT, serotonin transporter. (Adapted from Belmaker R, Agam
G: Major depressive disorder. N Engl J Med 2008;358:59.)
use is associated with reducing glutamatergic transmission, includ- Given the effect of antidepressants on the glutamate system,
ing the presynaptic release of glutamate in the hippocampus and there has been a growing interest in the development of pharmaceu-
cortical areas. Similarly, the chronic administration of antidepres- tical agents that might modulate the glutamate system. Ketamine
sants significantly reduces depolarization-evoked release of gluta- is a potent, high-affinity, noncompetitive N-methyl-d-aspartate
mate in animal models. Stress is known to enhance the release of (NMDA) receptor antagonist that has long been used in anesthe-
glutamate in rodents, and antidepressants inhibit stress-induced sia and is a common drug of abuse in some parts of the world. A
presynaptic release of glutamate in these models. number of preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated rapid