Page 586 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 586
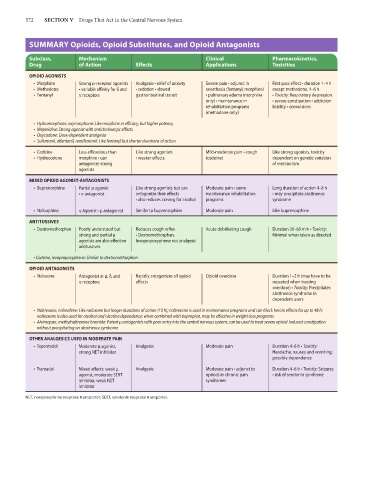
572 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
SUMMARY Opioids, Opioid Substitutes, and Opioid Antagonists
Subclass, Mechanism Clinical Pharmacokinetics,
Drug of Action Effects Applications Toxicities
OPIOID AGONISTS
• Morphine Strong μ-receptor agonists Analgesia • relief of anxiety Severe pain • adjunct in First-pass effect • duration 1–4 h
• Methadone • variable affinity for δ and • sedation • slowed anesthesia (fentanyl, morphine) except methadone, 4–6 h
• Fentanyl κ receptors gastrointestinal transit • pulmonary edema (morphine • Toxicity: Respiratory depression
only) • maintenance in • severe constipation • addiction
rehabilitation programs liability • convulsions
(methadone only)
• Hydromorphone, oxymorphone: Like morphine in efficacy, but higher potency
• Meperidine: Strong agonist with anticholinergic effects
• Oxycodone: Dose-dependent analgesia
• Sufentanil, alfentanil, remifentanil: Like fentanyl but shorter durations of action
• Codeine Less efficacious than Like strong agonists Mild-moderate pain • cough Like strong agonists, toxicity
• Hydrocodone morphine • can • weaker effects (codeine) dependent on genetic variation
antagonize strong of metabolism
agonists
MIXED OPIOID AGONIST-ANTAGONISTS
• Buprenorphine Partial μ agonist Like strong agonists but can Moderate pain • some Long duration of action 4–8 h
• κ antagonist antagonize their effects maintenance rehabilitation • may precipitate abstinence
• also reduces craving for alcohol programs syndrome
• Nalbuphine κ Agonist • μ antagonist Similar to buprenorphine Moderate pain Like buprenorphine
ANTITUSSIVES
• Dextromethorphan Poorly understood but Reduces cough reflex Acute debilitating cough Duration 30–60 min • Toxicity:
strong and partial μ • Dextromethorphan, Minimal when taken as directed
agonists are also effective levopropoxyphene not analgesic
antitussives
• Codeine, levopropoxyphene: Similar to dextromethorphan
OPIOID ANTAGONISTS
• Naloxone Antagonist at μ, δ, and Rapidly antagonizes all opioid Opioid overdose Duration 1–2 h (may have to be
κ receptors effects repeated when treating
overdose) • Toxicity: Precipitates
abstinence syndrome in
dependent users
• Naltrexone, nalmefene: Like naloxone but longer durations of action (10 h); naltrexone is used in maintenance programs and can block heroin effects for up to 48 h;
naltrexone is also used for alcohol and nicotine dependence; when combined with bupropion, may be effective in weight-loss programs
• Alvimopan, methylnaltrexone bromide: Potent μ antagonists with poor entry into the central nervous system; can be used to treat severe opioid-induced constipation
without precipitating an abstinence syndrome
OTHER ANALGESICS USED IN MODERATE PAIN
• Tapentadol Moderate μ agonist, Analgesia Moderate pain Duration 4–6 h • Toxicity:
strong NET inhibitor Headache; nausea and vomiting;
possible dependence
• Tramadol Mixed effects: weak μ Analgesia Moderate pain • adjunct to Duration 4–6 h • Toxicity: Seizures
agonist, moderate SERT opioids in chronic pain • risk of serotonin syndrome
inhibitor, weak NET syndromes
inhibitor
NET, norepinephrine reuptake transporter; SERT, serotonin reuptake transporter.