Page 715 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 715
CHAPTER 38 Thyroid & Antithyroid Drugs 701
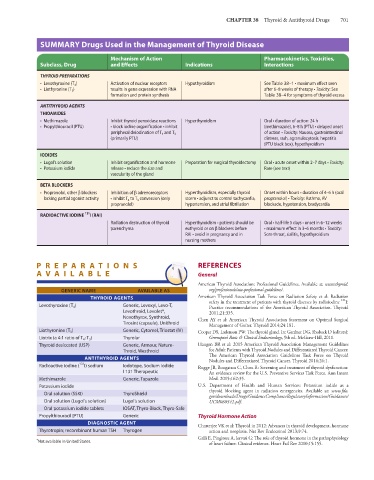
SUMMARY Drugs Used in the Management of Thyroid Disease
Mechanism of Action Pharmacokinetics, Toxicities,
Subclass, Drug and Effects Indications Interactions
THYROID PREPARATIONS
• Levothyroxine (T 4 ) Activation of nuclear receptors Hypothyroidism See Table 38–1 • maximum effect seen
• Liothyronine (T 3 ) results in gene expression with RNA after 6–8 weeks of therapy • Toxicity: See
formation and protein synthesis Table 38–4 for symptoms of thyroid excess
ANTITHYROID AGENTS
THIOAMIDES
• Methimazole Inhibit thyroid peroxidase reactions Hyperthyroidism Oral • duration of action: 24 h
• Propylthiouracil (PTU) • block iodine organification • inhibit (methimazole), 6–8 h (PTU) • delayed onset
peripheral deiodination of T 4 and T 3 of action • Toxicity: Nausea, gastrointestinal
(primarily PTU) distress, rash, agranulocytosis, hepatitis
(PTU black box), hypothyroidism
IODIDES
• Lugol’s solution Inhibit organification and hormone Preparation for surgical thyroidectomy Oral • acute onset within 2–7 days • Toxicity:
• Potassium iodide release • reduce the size and Rare (see text)
vascularity of the gland
BETA BLOCKERS
• Propranolol, other β blockers Inhibition of β adrenoreceptors Hyperthyroidism, especially thyroid Onset within hours • duration of 4–6 h (oral
lacking partial agonist activity • inhibit T 4 to T 3 conversion (only storm • adjunct to control tachycardia, propranolol) • Toxicity: Asthma, AV
propranolol) hypertension, and atrial fibrillation blockade, hypotension, bradycardia
RADIOACTIVE IODINE 131 I (RAI)
Radiation destruction of thyroid Hyperthyroidism • patients should be Oral • half-life 5 days • onset in 6–12 weeks
parenchyma euthyroid or on β blockers before • maximum effect in 3–6 months • Toxicity:
RAI • avoid in pregnancy and in Sore throat, sialitis, hypothyroidism
nursing mothers
PREP AR A TIONS REFERENCES
A V AIL ABLE General
American Thyroid Association: Professional Guidelines. Available at: www.thyroid.
GENERIC NAME AVAILABLE AS org/professionals/ata-professional-guidelines/.
THYROID AGENTS American Thyroid Association Task Force on Radiation Safety et al: Radiation
131
Levothyroxine (T 4 ) Generic, Levoxyl, Levo-T, safety in the treatment of patients with thyroid diseases by radioiodine I:
Practice recommendations of the American Thyroid Association. Thyroid
Levothroid, Levolet*, 2011;21:335.
Novothyrox, Synthroid, Chen AY et al: American Thyroid Association Statement on Optimal Surgical
Tirosint (capsule), Unithroid
Management of Goiter. Thyroid 2014;24:181.
Liothyronine (T 3 ) Generic, Cytomel, Triostat (IV) Cooper DS, Ladenson PW: The thyroid gland. In: Gardner DG, Shoback D (editors):
Liotrix (a 4:1 ratio of T 4 : T 3 ) Thyrolar Greenspan’s Basic & Clinical Endocrinology, 9th ed. McGraw-Hill, 2011.
Thyroid desiccated (USP) Generic, Armour, Nature- Haugen BR et al: 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines
Throid, Westhroid for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer:
ANTITHYROID AGENTS The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid
Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016;26:1.
Radioactive iodine ( 131 I) sodium Iodotope, Sodium Iodide Rugge JB, Bougatsos C, Chou R: Screening and treatment of thyroid dysfunction:
I 131 Therapeutic An evidence review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern
Methimazole Generic, Tapazole Med. 2015;162:35.
Potassium iodide U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Potassium iodide as a
Oral solution (SSKI) ThyroShield thyroid blocking agent in radiation emergencies. Available at: www.fda.
gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/
Oral solution (Lugol’s solution) Lugol’s solution UCM080542.pdf.
Oral potassium iodide tablets IOSAT, Thyro-Block, Thyro-Safe
Propylthiouracil [PTU] Generic Thyroid Hormone Action
DIAGNOSTIC AGENT Chatterjee VK et al: Thyroid in 2012: Advances in thyroid development, hormone
Thyrotropin; recombinant human TSH Thyrogen action and neoplasia. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2013;9:74.
Galli E, Pingitore A, Iervasi G: The role of thyroid hormone in the pathophysiology
* Not available in United States.
of heart failure: Clinical evidence. Heart Fail Rev 2010;15:155.