Page 888 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 888
874 SECTION VIII Chemotherapeutic Drugs
gp41
gp120
Blocked by CCR5
receptor antagonists
Host cell membrane
Binding
Chemokine receptors
CD4 Fusion and
Blocked by uncoating
fusion inhibitors
RNA
Blocked by Reverse
NRTIs, NNRTIs transcription
DNA
Integration
Blocked by integrase inhibitors
Transcription Translation
RNA Virion
assembly
Nucleus
Budding and
maturation
Blocked by protease
inhibitors
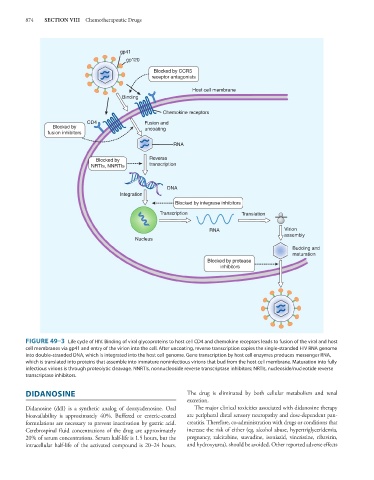
FIGURE 49–3 Life cycle of HIV. Binding of viral glycoproteins to host cell CD4 and chemokine receptors leads to fusion of the viral and host
cell membranes via gp41 and entry of the virion into the cell. After uncoating, reverse transcription copies the single-stranded HIV RNA genome
into double-stranded DNA, which is integrated into the host cell genome. Gene transcription by host cell enzymes produces messenger RNA,
which is translated into proteins that assemble into immature noninfectious virions that bud from the host cell membrane. Maturation into fully
infectious virions is through proteolytic cleavage. NNRTIs, nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors; NRTIs, nucleoside/nucleotide reverse
transcriptase inhibitors.
DIDANOSINE The drug is eliminated by both cellular metabolism and renal
excretion.
Didanosine (ddI) is a synthetic analog of deoxyadenosine. Oral The major clinical toxicities associated with didanosine therapy
bioavailability is approximately 40%. Buffered or enteric-coated are peripheral distal sensory neuropathy and dose-dependent pan-
formulations are necessary to prevent inactivation by gastric acid. creatitis. Therefore, co-administration with drugs or conditions that
Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of the drug are approximately increase the risk of either (eg, alcohol abuse, hypertriglyceridemia,
20% of serum concentrations. Serum half-life is 1.5 hours, but the pregnancy, zalcitabine, stavudine, isoniazid, vincristine, ribavirin,
intracellular half-life of the activated compound is 20–24 hours. and hydroxyurea), should be avoided. Other reported adverse effects