Page 201 - StudyBook.pdf
P. 201
Communication Security: Wireless • Chapter 4 185
WEP uses the RC4 encryption algorithm, a stream cipher developed by Ron
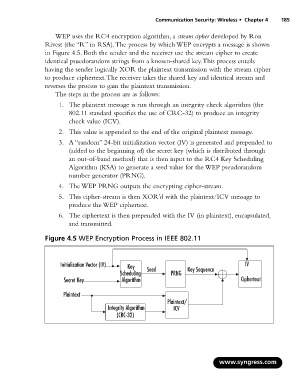
Rivest (the “R” in RSA).The process by which WEP encrypts a message is shown
in Figure 4.5. Both the sender and the receiver use the stream cipher to create
identical psuedorandom strings from a known-shared key.This process entails
having the sender logically XOR the plaintext transmission with the stream cipher
to produce ciphertext.The receiver takes the shared key and identical stream and
reverses the process to gain the plaintext transmission.
The steps in the process are as follows:
1. The plaintext message is run through an integrity check algorithm (the
802.11 standard specifies the use of CRC-32) to produce an integrity
check value (ICV).
2. This value is appended to the end of the original plaintext message.
3. A “random” 24-bit initialization vector (IV) is generated and prepended to
(added to the beginning of) the secret key (which is distributed through
an out-of-band method) that is then input to the RC4 Key Scheduling
Algorithm (KSA) to generate a seed value for the WEP pseudorandom
number generator (PRNG).
4. The WEP PRNG outputs the encrypting cipher-stream.
5. This cipher-stream is then XOR’d with the plaintext/ICV message to
produce the WEP ciphertext.
6. The ciphertext is then prepended with the IV (in plaintext), encapsulated,
and transmitted.
Figure 4.5 WEP Encryption Process in IEEE 802.11
Initialization Vector (IV) Key IV
Scheduling Seed PRNG Key Sequence
Secret Key Algorithm Ciphertext
Plaintext
Plaintext/
Integrity Algorithm ICV
(CRC-32)
www.syngress.com