Page 77 - StudyBook.pdf
P. 77
General Security Concepts: Attacks • Chapter 2 61
accept any legitimate requests, so it becomes unavailable, thus achieving the pur-
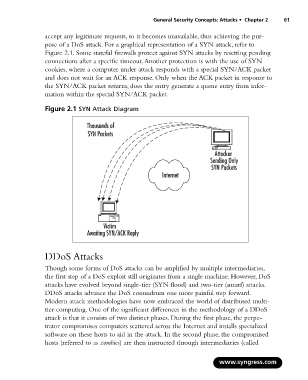
pose of a DoS attack. For a graphical representation of a SYN attack, refer to
Figure 2.1. Some stateful firewalls protect against SYN attacks by resetting pending
connections after a specific timeout.Another protection is with the use of SYN
cookies, where a computer under attack responds with a special SYN/ACK packet
and does not wait for an ACK response. Only when the ACK packet in response to
the SYN/ACK packet returns, does the entry generate a queue entry from infor-
mation within the special SYN/ACK packet.
Figure 2.1 SYN Attack Diagram
Thousands of
SYN Packets
Attacker
Sending Only
SYN Packets
Internet
Victim
Awaiting SYN/ACK Reply
DDoS Attacks
Though some forms of DoS attacks can be amplified by multiple intermediaries,
the first step of a DoS exploit still originates from a single machine. However, DoS
attacks have evolved beyond single-tier (SYN flood) and two-tier (smurf) attacks.
DDoS attacks advance the DoS conundrum one more painful step forward.
Modern attack methodologies have now embraced the world of distributed multi-
tier computing. One of the significant differences in the methodology of a DDoS
attack is that it consists of two distinct phases. During the first phase, the perpe-
trator compromises computers scattered across the Internet and installs specialized
software on these hosts to aid in the attack. In the second phase, the compromised
hosts (referred to as zombies) are then instructed through intermediaries (called
www.syngress.com