Page 23 - March 2020 - WT Site
P. 23
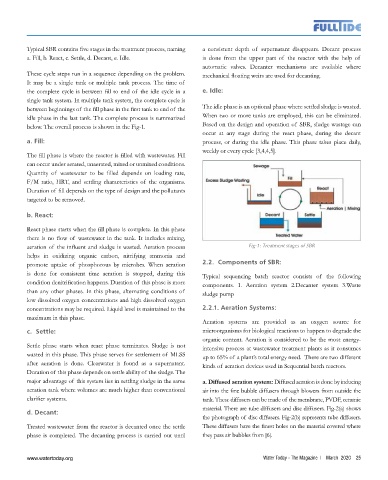
Typical SBR contains five stages in the treatment process, naming a consistent depth of supernatant disappears. Decant process
a. Fill, b. React, c. Settle, d. Decant, e. Idle. is done from the upper part of the reactor with the help of
automatic valves. Decanter mechanisms are available where
These cycle steps run in a sequence depending on the problem. mechanical floating weirs are used for decanting.
It may be a single tank or multiple tank process. The time of
the complete cycle is between fill to end of the idle cycle in a e. Idle:
single tank system. In multiple tank system, the complete cycle is
between beginnings of the fill phase in the first tank to end of the The idle phase is an optional phase where settled sludge is wasted.
idle phase in the last tank. The complete process is summarized When two or more tanks are employed, this can be eliminated.
below. The overall process is shown in the Fig-1. Based on the design and operation of SBR, sludge wastage can
occur at any stage during the react phase, during the decant
a. Fill: process, or during the idle phase. This phase takes place daily,
weekly or every cycle [3,4,4,5].
The fill phase is where the reactor is filled with wastewater. Fill
can occur under aerated, unaerated, mixed or unmixed conditions.
Quantity of wastewater to be filled depends on loading rate,
F/M ratio, HRT, and settling characteristics of the organisms.
Duration of fill depends on the type of design and the pollutants
targeted to be removed.
b. React:
React phase starts when the fill phase is complete. In this phase
there is no flow of wastewater in the tank. It includes mixing,
aeration of the influent and sludge is wasted. Aeration process Fig-1: Treatment stages of SBR
helps in oxidizing organic carbon, nitrifying ammonia and
promote uptake of phosphorous by microbes. When aeration 2.2. Components of SBR:
is done for consistent time aeration is stopped, during this Typical sequencing batch reactor consists of the following
condition denitrification happens. Duration of this phase is more components. 1. Aeration system 2.Decanter system 3.Waste
than any other phases. In this phase, alternating conditions of sludge pump
low dissolved oxygen concentrations and high dissolved oxygen
concentrations may be required. Liquid level is maintained to the 2.2.1. Aeration Systems:
maximum in this phase.
Aeration systems are provided as an oxygen source for
c. Settle: microorganisms for biological reactions to happen to degrade the
organic content. Aeration is considered to be the most energy-
Settle phase starts when react phase terminates. Sludge is not intensive process at wastewater treatment plants as it consumes
wasted in this phase. This phase serves for settlement of MLSS up to 65% of a plant’s total energy need. There are two different
after aeration is done. Clearwater is found as a supernatant. kinds of aeration devices used in Sequential batch reactors.
Duration of this phase depends on settle ability of the sludge. The
major advantage of this system lies in settling sludge in the same a. Diffused aeration system: Diffused aeration is done by inducing
aeration tank where volumes are much higher than conventional air into the fine bubble diffusers through blowers from outside the
clarifier systems. tank. These diffusers can be made of the membrane, PVDF, ceramic
material. There are tube diffusers and disc diffusers. Fig-2(a) shows
d. Decant:
the photograph of disc diffusers. Fig-2(b) represents tube diffusers.
Treated wastewater from the reactor is decanted once the settle These diffusers have the finest holes on the material covered where
phase is completed. The decanting process is carried out until they pass air bubbles from [6].
Water Today - The Magazine l March 2020 25