Page 14 - Human anatomy COMPLETELY DONE1
P. 14
HUMAN SKELETAL MUSCLES
Skeletal muscles by weight prevail over other muscles of the body (smooth
muscles of internal organs and the heart). Skeletal musculature can reach 50% of the
total body weight.
In the human body, depending on the method of counting, there are about 600
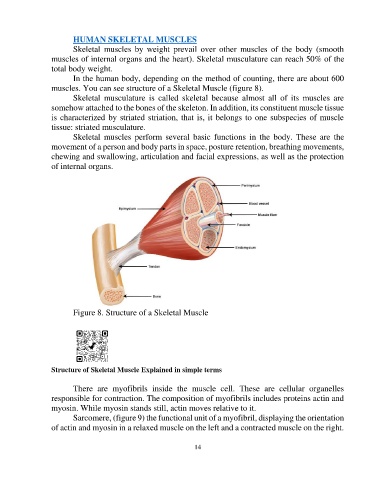
muscles. You can see structure of a Skeletal Muscle (figure 8).
Skeletal musculature is called skeletal because almost all of its muscles are
somehow attached to the bones of the skeleton. In addition, its constituent muscle tissue
is characterized by striated striation, that is, it belongs to one subspecies of muscle
tissue: striated musculature.
Skeletal muscles perform several basic functions in the body. These are the
movement of a person and body parts in space, posture retention, breathing movements,
chewing and swallowing, articulation and facial expressions, as well as the protection
of internal organs.
Figure 8. Structure of a Skeletal Muscle
Structure of Skeletal Muscle Explained in simple terms
There are myofibrils inside the muscle cell. These are cellular organelles
responsible for contraction. The composition of myofibrils includes proteins actin and
myosin. While myosin stands still, actin moves relative to it.
Sarcomere, (figure 9) the functional unit of a myofibril, displaying the orientation
of actin and myosin in a relaxed muscle on the left and a contracted muscle on the right.
14