Page 124 - Deception at work all chapters EBook
P. 124
The Human Mind 65
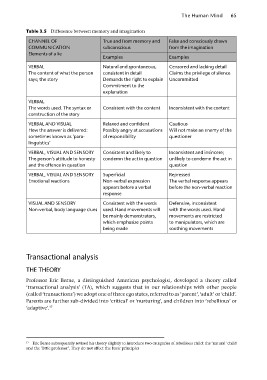
Table 3.5 Difference between memory and imagination
CHANNEL OF True and from memory and False and consciously drawn
COMMUNICATION subconscious from the imagination
Elements of a lie
Examples Examples
VERBAL Natural and spontaneous, Censored and lacking detail
The content of what the person consistent in detail Claims the privilege of silence
says; the story Demands the right to explain Uncommitted
Commitment to the
explanation
VERBAL Consistent with the content Inconsistent with the content
The words used. The syntax or
construction of the story
VERBAL AND VISUAL Relaxed and confident Cautious
How the answer is delivered: Possibly angry at accusations Will not make an enemy of the
sometimes known as ‘para- of responsibility questioner
linguistics’
VERBAL, VISUAL AND SENSORY Consistent and likely to Inconsistent and insincere;
The person’s attitude to honesty condemn the act in question unlikely to condemn the act in
and the offence in question question
VERBAL, VISUAL AND SENSORY Superficial Repressed
Emotional reactions Non-verbal expression The verbal response appears
appears before a verbal before the non-verbal reaction
response
VISUAL AND SENSORY Consistent with the words Defensive, inconsistent
Non-verbal, body language clues used. Hand movements will with the words used. Hand
be mainly demonstrators, movements are restricted
which emphasize points to manipulators, which are
being made soothing movements
Transactional analysis
THE THEORY
Professor Eric Berne, a distinguished American psychologist, developed a theory called
‘transactional analysis’ (TA), which suggests that in our relationships with other people
(called ‘transactions’) we adopt one of three ego states, referred to as ‘parent’, ‘adult’ or ‘child’.
Parents are further sub-divided into ‘critical’ or ‘nurturing’, and children into ‘rebellious’ or
‘adaptive’.17
17 Eric Berne subsequently revised his theory slightly to introduce two categories of rebellious child: the ‘natural’ child
and the ‘little professor’. They do not affect the basic principles