Page 75 - Deception at work all chapters EBook
P. 75
116 Deception at Work
MORE OF OJ SIMPSON I was getting my phone and everything off
it, when I just pulled it out of the gate there
In answering questions about the unusual … it’s like a tight turn.’ The change of tense
way in which the Bronco had been parked suggests that the story is untrue, as does
Mr Simpson said, ‘Well, it’s parked because the preposition ‘off’ rather than ‘from’ (the
… I don’t know if it’s a funny angle or what. Bronco).
It’s parked because when I was hustling and
the end of the day to get all my stuff, and
PAST TENSE FOR LIVING PEOPLE
In a recent high-profile case, three children lovely kids’ etc. The mother, however,
had been abducted and the fear was that referred to them in the past tense: ‘they
they had been murdered. The mother and were home loving and caring’, revealing
father appeared on television appealing for that she knew they were dead. She was later
their kids to be returned. He consistently convicted of their murder.
referred to them in the present tense: ‘are
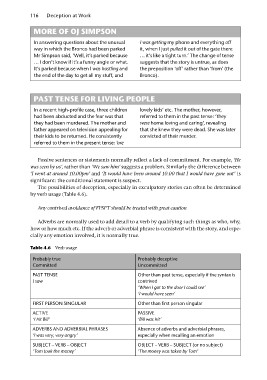
Passive sentences or statements normally reflect a lack of commitment. For example, ‘He
was seen by us’, rather than ‘We saw him’ suggests a problem. Similarly the difference between
‘I went at around 10.00pm’ and ‘It would have been around 10.00 that I would have gone out ’ is
significant: the conditional statement is suspect.
The possibilities of deception, especially in exculpatory stories can often be determined
by verb usage (Table 4.6).
Any contrived avoidance of FPSPT should be treated with great caution
Adverbs are normally used to add detail to a verb by qualifying such things as who, why,
how or how much etc. If the adverb or adverbial phrase is consistent with the story, and espe-
cially any emotion involved, it is normally true.
Table 4.6 Verb usage Probably deceptive
Uncommitted
Probably true
Committed Other than past tense, especially if the syntax is
PAST TENSE contrived
I saw ‘When I got to the door I could see’
‘I would have seen’
FIRST PERSON SINGULAR
ACTIVE Other than first person singular
‘I hit Bill’
ADVERBS AND ADVERBIAL PHRASES PASSIVE
‘I was very, very angry’ ‘Bill was hit’
SUBJECT – VERB – OBJECT
‘Tom took the money’ Absence of adverbs and adverbial phrases,
especially when recalling an emotion
OBJECT – VERB – SUBJECT (or no subject)
‘The money was taken by Tom’