Page 82 - Deception at work all chapters EBook
P. 82
Signs of Deception 123
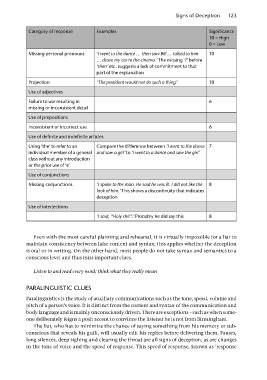
Category of response Examples Significance
10 = High
0 = Low
Missing personal pronouns ‘I went to the dance … then saw Bill … talked to him 10
… drove my car to the cinema.’ The missing ‘I’ before
‘then’ etc. suggests a lack of commitment to that
part of the explanation
Projection ‘The president would not do such a thing’ 10
Use of adjectives
Failure to use resulting in 6
missing or inconsistent detail
Use of prepositions
Inconsistent or incorrect use 6
Use of definite and indefinite articles
Using ‘the’ to refer to an Compare the difference between ‘I went to the dance 7
individual member of a general and saw a girl’ to ‘I went to a dance and saw the girl’
class without any introduction
or the prior use of ‘a’
Use of conjunctions
Missing conjunctions ‘I spoke to the man. He said he was ill. I did not like the 8
look of him.’ This shows a discontinuity that indicates
deception
Use of interjections
‘I said, “Holy shit”.’ Probably he did say this 8
Even with the most careful planning and rehearsal, it is virtually impossible for a liar to
maintain consistency between false content and syntax; this applies whether the deception
is oral or in writing. On the other hand, most people do not take syntax and semantics to a
conscious level and thus miss important clues.
Listen to and read every word; think what they really mean
PARALINGUISTIC CLUES
Paralinguistics is the study of auxiliary communications such as the tone, speed, volume and
pitch of a person’s voice. It is distinct from the content and syntax of the communication and
body language and is mainly unconsciously driven. There are exceptions – such as when some-
one deliberately feigns a posh accent to convince the listener he is not from Birmingham.
The liar, who has to minimize the chance of saying something from his memory or sub-
conscious that reveals his guilt, will usually edit his replies before delivering them. Pauses,
long silences, deep sighing and clearing the throat are all signs of deception, as are changes
in the tone of voice and the speed of response. This speed of response, known as ‘response