Page 172 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 172
158 MECHATRONICS
From the desired motion profile specification, we determine the maximum speed the
actuator must deliver using the kinematic relations. In order to design an optimal motion
control axis, the actuator sizing and the motion conversion mechanism (effective gear ratio)
should be considered together. It is possible that a very small gear ratio may require a motor
with very large torque requirement, and yet run at very low speeds, hence making use of a
small part of the power capacity of the motor. An increased gear ratio would then require a
smaller torque motor and that the motor would operate at higher speeds on average, hence
making more use of the available power of the motor.
Once the torque requirements are known, the drive current and power supply voltage
requirements can be directly determined for a given electric motor-drive system. Similarly,
for hydraulic actuators, once the force requirements are determined, we would pick the
supply pressure and determine the diameter of the linear cylinder. The speed requirement
would determine the flow rate. Once these are known, then the size of the valve and pump
can be determined.
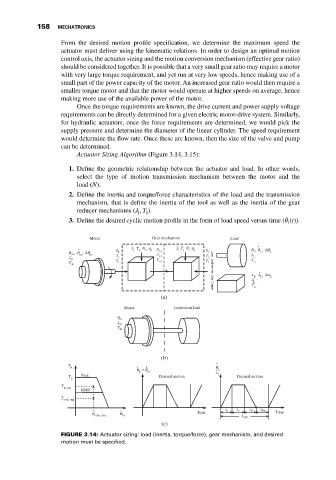
Actuator Sizing Algorithm (Figure 3.14, 3.15):
1. Define the geometric relationship between the actuator and load. In other words,
select the type of motion transmission mechanism between the motor and the
load (N).
2. Define the inertia and torque/force characteristics of the load and the transmission
mechanism, that is define the inertia of the tool as well as the inertia of the gear
reducer mechanisms (J , T ).
l
l
̇
3. Define the desired cyclic motion profile in the form of load speed versus time ( (t)).
l
Motor Gear mechanism Load
J T N η S J T N η ι θθ , Δθ
,
1 1
, θ , Δθ S L 1 1 i-1 i i i S i 1 L L
θ m J J
m m J i-1 J
T T T
J m L T i L
T m L i-1 i L
x , x , Δx L
1
L
J L
T
L
(a)
Motor Equivalent load
θ m
J m
T m
(b)
T
m θ
θ L = θ m x L
T p Peak Desired motion 1 Desired motion
T
p, req
RMS
T rms, req
t a t r t d t dw
θ θ Time Time
max, req m
t cyc
(c)
FIGURE 3.14: Actuator sizing: load (inertia, torque/force), gear mechanism, and desired
motion must be specified.