Page 173 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 173
MECHANISMS FOR MOTION TRANSMISSION 159
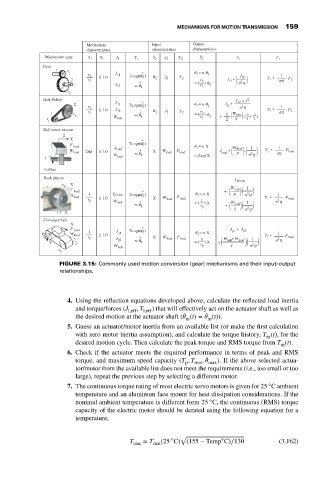
Mechanism Input Output
characteristics characteristics characteristics
Mechanism type n 1 η 1 J 1 T 1 S 2 2 J T 2 S 1 J 1 T 1
Gear
1 r
1 θ 1 = n θ 2
2 r ≤ 1.0 J r1 Tc.sgn( ) θ T J 1
r1 ( )
θ 1
2 1 r 2 2 J 2 2 r J + 2 r2 i T + nη T 2
J r2 +c θ 1 = ( ) θ 2 n η
1 r
r
2
Belt-Pulley J J r2 + J 2
2 r1 Tc.sgn( ) θ 1 = n θ 2 J r1 +
2 r ≤ 1.0 J θ 1 n η i T + 1 T
2
2 r
W
1 r 1 r r2 θ θ 2 2 J T 2 = ( ) θ 2 1 ( ) r 2 r 2 nη 2
belt
g
r 2 W belt +c 1 1 r + ( + )
1
2
2
1
Ball screw or cam
2
X
F Tc.sgn( )
θ 1
load J θ 1 = n X W 1 1
load
π
+
W load 2 p ≤ 1.0 lead X W load F load J load ( ) ( ) i T + F load
g
θ
2
π
W +c 1 = ( ) X n η nη
2 p
1 load
θ π
X= /2 p
Rack pinion J pinion
p r X
1 W 1
F rack
load + ( ) ( )
2
W 1 J pinion Tc.sgn( ) θ 1 = n X g n η 1
θ 1
load ≤ 1.0 X W F i T + F
p r W load load 1 W n η load
2
rack
1
load
+c θ 1 = ( ) X + ( ) ( )
p r
g
2
2 X n η
Conveyor belt
X
F load J Tc.sgn( ) J p1 + J p2
1 W load 1 p r ≤ 1.0 p1 θ 1 X W F θ 1 = n X i T + 1 F load
W
belt W
1
1
+
2
load
p r 2 J p2 +c θ 1 load load = ( ) X ( ) ( ) n η
+
2
W p r g n η
p r belt
FIGURE 3.15: Commonly used motion conversion (gear) mechanisms and their input–output
relationships.
4. Using the reflection equations developed above, calculate the reflected load inertia
and torque/forces (J l,eff , T l,eff ) that will effectively act on the actuator shaft as well as
̇
̇
the desired motion at the actuator shaft ( (t) = (t)).
in
m
5. Guess an actuator/motor inertia from an available list (or make the first calculation
with zero motor inertia assumption), and calculate the torque history, T (t), for the
m
desired motion cycle. Then calculate the peak torque and RMS torque from T (t).
m
6. Check if the actuator meets the required performance in terms of peak and RMS
torque, and maximum speed capacity (T , T rms , ̇ max ). If the above selected actua-
p
tor/motor from the available list does not meet the requirements (i.e., too small or too
large), repeat the previous step by selecting a different motor.
◦
7. The continuous torque rating of most electric servo motors is given for 25 C ambient
temperature and an aluminum face mount for heat dissipation considerations. If the
◦
nominal ambient temperature is different form 25 C, the continuous (RMS) torque
capacity of the electric motor should be derated using the following equation for a
temperature,
√ ◦
◦
T rms = T rms (25 C) (155 − Temp C)∕130 (3.162)