Page 734 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 734
720 MECHATRONICS
Operator interface
network communication
Offline programming
Power supply and amplifier
PLC
C I O Motion controller
P
S P N U
U T P.S.
PC + Gear/motion
Command + K Motor transmission
generator _ PID _ PID mechanism
d Current loop Sensor
Other I/O ≈ (.)
dt
Position loop Velocity loop
Hand held
programmer
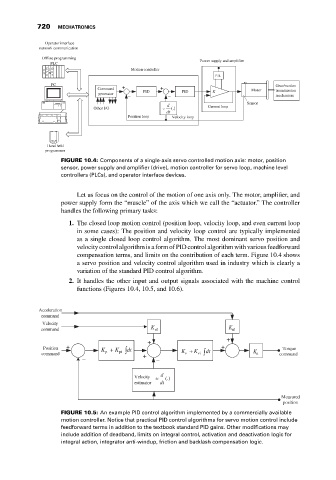
FIGURE 10.4: Components of a single-axis servo controlled motion axis: motor, position
sensor, power supply and amplifier (drive), motion controller for servo loop, machine level
controllers (PLCs), and operator interface devices.
Let us focus on the control of the motion of one axis only. The motor, amplifier, and
power supply form the “muscle” of the axis which we call the “actuator.” The controller
handles the following primary tasks:
1. The closed loop motion control (position loop, velocity loop, and even current loop
in some cases): The position and velocity loop control are typically implemented
as a single closed loop control algorithm. The most dominant servo position and
velocity control algorithm is a form of PID control algorithm with various feedforward
compensation terms, and limits on the contribution of each term. Figure 10.4 shows
a servo position and velocity control algorithm used in industry which is clearly a
variation of the standard PID control algorithm.
2. It handles the other input and output signals associated with the machine control
functions (Figures 10.4, 10.5, and 10.6).
Acceleration
command
Velocity
command K vf K af
+
+
Position + K K dt + Torque
command p pi K v K vi dt K a command
_ + _
d
Velocity (.)
estimator dt
Measured
position
FIGURE 10.5: An example PID control algorithm implemented by a commercially available
motion controller. Notice that practical PID control algorithms for servo motion control include
feedforward terms in addition to the textbook standard PID gains. Other modifications may
include addition of deadband, limits on integral control, activation and deactivation logic for
integral action, integrator anti-windup, friction and backlash compensation logic.