Page 736 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 736
722 MECHATRONICS
A E M
C
Digital I/O A E M
C
A E M
C
(a)
A E M
C
High speed
communication bus
(i.e., Sercos, Ethernet, USB)
A E M
C
A E M
C
(b)
Multi axis controller
A E M
DSP
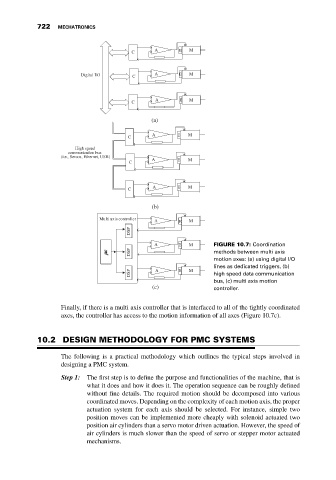
A E M FIGURE 10.7: Coordination
DSP methods between multi axis
motion axes: (a) using digital I/O
lines as dedicated triggers, (b)
DSP A E M high speed data communication
bus, (c) multi axis motion
(c) controller.
Finally, if there is a multi axis controller that is interfaced to all of the tightly coordinated
axes, the controller has access to the motion information of all axes (Figure 10.7c).
10.2 DESIGN METHODOLOGY FOR PMC SYSTEMS
The following is a practical methodology which outlines the typical steps involved in
designing a PMC system.
Step 1: The first step is to define the purpose and functionalities of the machine, that is
what it does and how it does it. The operation sequence can be roughly defined
without fine details. The required motion should be decomposed into various
coordinated moves. Depending on the complexity of each motion axis, the proper
actuation system for each axis should be selected. For instance, simple two
position moves can be implemented more cheaply with solenoid actuated two
position air cylinders than a servo motor driven actuation. However, the speed of
air cylinders is much slower than the speed of servo or stepper motor actuated
mechanisms.