Page 64 - Org 3 theoritical book 2024-25
P. 64
Clinical Pharmacy PharmD - 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-3 (PC 305)
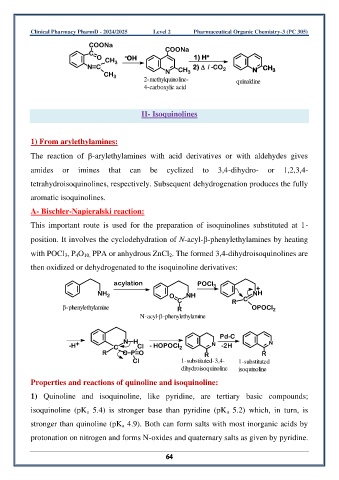
COONa
C COONa
O CH - OH 1) H +
N C 3 CH 2) / -CO 2 N CH 3
CH 3 N 3
2-methylquinoline- quinaldine
4-carboxylic acid
II- Isoquinolines
1) From arylethylamines:
The reaction of -arylethylamines with acid derivatives or with aldehydes gives
amides or imines that can be cyclized to 3,4-dihydro- or 1,2,3,4-
tetrahydroisoquinolines, respectively. Subsequent dehydrogenation produces the fully
aromatic isoquinolines.
A- Bischler-Napieralski reaction:
This important route is used for the preparation of isoquinolines substituted at 1-
position. It involves the cyclodehydration of N-acyl--phenylethylamines by heating
with POCl 3, P 4O 10, PPA or anhydrous ZnCl 2. The formed 3,4-dihydroisoquinolines are
then oxidized or dehydrogenated to the isoquinoline derivatives:
acylation POCl 3
+
NH 2 O NH NH
C R C
-phenylethylamine R OPOCl 2
N-acyl--phenylethylamine
Pd-C
-H + C N H Cl - HOPOCl 2 N -2H N
R O P O R R
Cl 1-substituted-3,4- 1-substituted
dihydroisoquinoline isoquinoline
Properties and reactions of quinoline and isoquinoline:
1) Quinoline and isoquinoline, like pyridine, are tertiary basic compounds;
isoquinoline (pK a 5.4) is stronger base than pyridine (pK a 5.2) which, in turn, is
stronger than quinoline (pK a 4.9). Both can form salts with most inorganic acids by
protonation on nitrogen and forms N-oxides and quaternary salts as given by pyridine.