Page 65 - Org 3 theoritical book 2024-25
P. 65
Clinical Pharmacy PharmD - 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-3 (PC 305)
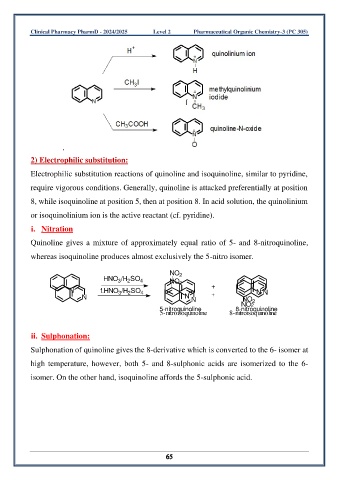
2) Electrophilic substitution:
Electrophilic substitution reactions of quinoline and isoquinoline, similar to pyridine,
require vigorous conditions. Generally, quinoline is attacked preferentially at position
8, while isoquinoline at position 5, then at position 8. In acid solution, the quinolinium
or isoquinolinium ion is the active reactant (cf. pyridine).
i. Nitration
Quinoline gives a mixture of approximately equal ratio of 5- and 8-nitroquinoline,
whereas isoquinoline produces almost exclusively the 5-nitro isomer.
NO 2
HNO /H SO 4 NO 2
2
3
N f.HNO /H SO 4 + N N
2
3
N N N NO 2
NO2
5-nitroquinoline 8-nitroquinoline
5-nitroisoquinoline 8-nitroisoquinoline
ii. Sulphonation:
Sulphonation of quinoline gives the 8-derivative which is converted to the 6- isomer at
high temperature, however, both 5- and 8-sulphonic acids are isomerized to the 6-
isomer. On the other hand, isoquinoline affords the 5-sulphonic acid.