Page 81 - Pharmaceutical Organic Chemmistry-3 (Theoritical book) 24-25
P. 81
Clinical Pharmacy PharmD - 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-3 (PC 305)
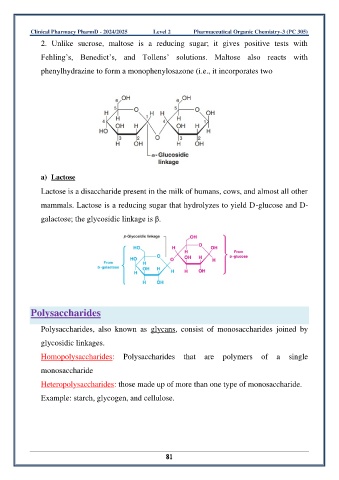
2. Unlike sucrose, maltose is a reducing sugar; it gives positive tests with
Fehling’s, Benedict’s, and Tollens’ solutions. Maltose also reacts with
phenylhydrazine to form a monophenylosazone (i.e., it incorporates two
a) Lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide present in the milk of humans, cows, and almost all other
mammals. Lactose is a reducing sugar that hydrolyzes to yield D-glucose and D-
galactose; the glycosidic linkage is β.
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides, also known as glycans, consist of monosaccharides joined by
glycosidic linkages.
Homopolysaccharides: Polysaccharides that are polymers of a single
monosaccharide
Heteropolysaccharides: those made up of more than one type of monosaccharide.
Example: starch, glycogen, and cellulose.