Page 84 - Pharmaceutical Organic Chemmistry-3 (Theoritical book) 24-25
P. 84
Clinical Pharmacy PharmD - 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-3 (PC 305)
Proteins & Amino acids
• Proteins are polyamides, and their monomeric units are composed of about 20 different a-amino acids.
• The exact sequence of the different amino acids along the protein chain is called
the primary structure of the protein.
• Folding of the polyamide chain gives rise to higher levels of complexity called
the secondary and tertiary structures of the protein.
• Hydrolysis of proteins with acid or base yields a mixture of amino acids.
Amino Acids:Essential Amino Acids:
Amino acids can be synthesized by all living organisms, plants and animals.
Many higher animals can’t synthesize all of the amino acids they need for their
proteins. Thus, they require certain amino acids as a part of their diet. For adult
humans there are eight essential amino acids.
Amino Acids as Dipolar Ions
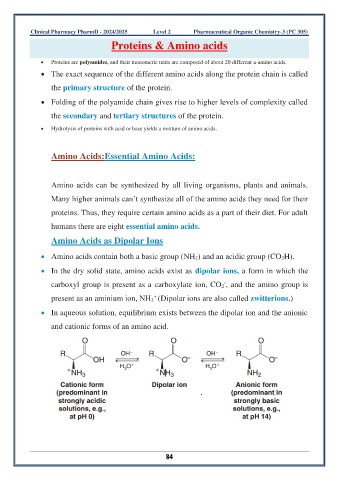
• Amino acids contain both a basic group (NH 2) and an acidic group (CO 2H).
• In the dry solid state, amino acids exist as dipolar ions, a form in which the
-
carboxyl group is present as a carboxylate ion, CO 2 , and the amino group is
present as an aminium ion, NH 3 (Dipolar ions are also called zwitterions.)
+
• In aqueous solution, equilibrium exists between the dipolar ion and the anionic
and cationic forms of an amino acid.