Page 170 - Industrial Tools Catalog (1)
P. 170
Thread tools \ Technical introduction – female thread production
Thread production process at a glance
Screw tapping Thread forming Milling cutter
Process reliability ○ + ++
Surface quality ○ ++ +
Machining speed + ++ ○
Service life ○ ++ +
Flexibility/universal use ○ + ++
Thread depth ○ ++ ++
○ = limited suitability | + = well suited | ++ = very well suited
Tolerances for threads
standards ensure that male and female threads of the desired form fit together. depending on the application, the appropriate tolerance must be taken into account
for the screw tap or thread former. in thread milling, the tolerance can be produced as desired using radius correction. the graphic shows the different tolerance
classes and their use.
DIN EN 22857 DIN 802 part 1
Application class of the screw tap Tolerance range of nut thread to Tolerance class Technical application
be cut
Name Identification of the screw tap
Class 1 ISO 1 4H 5H 4H Screw connection with little play
Class 2 ISO 2 6H 6H Standard screw connection
Class 3 ISO 3 6G 6G Screw connection with a lot of play
– – 7 As a preventive measure against warping in heat treatment
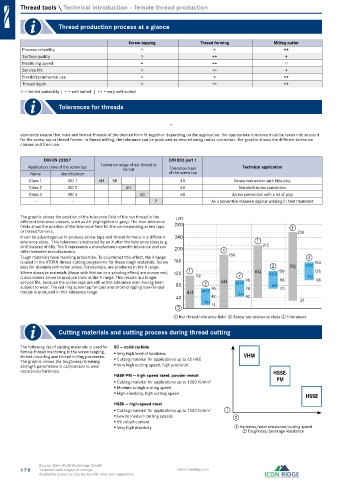
The graphic shows the position of the tolerance field of the nut thread in the µm
different tolerance classes, such as 6H (highlighted in grey). The blue tolerance
fields show the position of the tolerance field for the corresponding screw taps 280 1
or thread formers. 256
It can be advantageous to produce screw taps and thread formers in a different 240
tolerance class. This tolerance is indicated by an X after the tolerance class (e.g. 1
6HX instead of 6H). The X represents a manufacturer-specific tolerance and can 200 212
differ between manufacturers. 1
Tough materials have recoiling properties. To counteract this effect, the X range 180 2
is used in the ATORN thread cutting programme for these tough materials. Screw 160 154
taps for titanium and nickel alloys, for example, are produced in the X range. 2 7G 7GX
Where abrasive materials (those with friction or a grinding effect) are concerned, 120 1 6G 6GX 126 126
it also makes sense to produce tools in the X range. This results in a longer 112 2 7G
service life, because the screw taps are still within tolerance even having been 2 6H 6HX 98 98 98
subject to wear. The red ring screw tap for cast and short-chipping non-ferrous 80 70 70 6G 70
metals is produced in this tolerance range. 4H 4HX 6H
40 42 42
4H 14 32
3
① Nut thread tolerance field ② Screw tap tolerance class ③ Tolerances
Cutting materials and cutting process during thread cutting
The following list of cutting materials is used for SC — solid carbide
female thread machining in the screw tapping, Very high level of hardness
thread moulding and thread milling processes. VHM
The graphic shows the toughness/breaking Cutting material for applications up to 65 HRC
strength parameters in comparison to wear Very high cutting speed, high precision
resistance/hardness. HSSE-
HSSE-PM — high speed steel, powder metal
Cutting material for applications up to 1300 N/mm 2 PM
Medium to high cutting speed
High elasticity, high cutting speed
HSSE
HSSE — high-speed steel
Cutting material for applications up to 1300 N/mm 2 1
Low to medium cutting speeds 2
5% cobalt content
Very high elasticity ① Hardness/wear resistance/cutting speed
② Toughness/breakage resistance
Source: Hahn+Kolb Werkzeuge GmbH
170 Technical data subject to change. www.iconridge.com
Availability subject to country specific rules and regulations.