Page 36 - Anuario Abrasca 19_20
P. 36
Matéria de capa Cover story
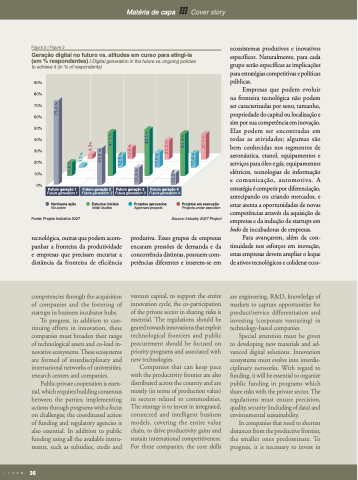
Figura 3 / Figure 3
Geração digital no futuro vs. atitudes em curso para atingi-la (em % respondentes) / Digital generation in the future vs. ongoing policies to achieve it (in % of respondents)
ecossistemas produtivos e inovativos específicos. Naturalmente, para cada grupo serão específicas as implicações para estratégias competitivas e políticas públicas.
Empresas que podem evoluir na fronteira tecnológica não podem ser caracterizadas por setor, tamanho, propriedade do capital ou localização e sim por sua competência em inovação. Elas podem ser encontradas em todas as atividades; algumas são bem conhecidas nos segmentos de aeronáutica, etanol, equipamentos e serviços para óleo e gás, equipamentos elétricos, tecnologias de informação e comunicação, automotiva. A estratégia é competir por diferenciação, antecipando ou criando mercados, e estar atenta a oportunidades de novas competências através da aquisição de empresas e da indução de startups em hubs de incubadoras de empresas.
Para avançarem, além da con- tinuidade nos esforços em inovação, estas empresas devem ampliar o leque de ativos tecnológicos e coliderar ecos-
90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10%
0%
Futuro geração 1
Future generation 1
Futuro geração 2
Future generation 2
Futuro geração 3
Future generation 3
Futuro geração 4
Future generation 4
Nenhuma ação
No action
Estudos iniciais
Initial studies
Projetos aprovados
Approved projects
Projetos em execução
Projects under execution Source: Industry 2027 Project
Fonte: Projeto Indústria 2027
tecnológica, outras que podem acom- panhar a fronteira da produtividade e empresas que precisam encurtar a distância da fronteira de eficiência
produtiva. Esses grupos de empresas encaram pressões de demanda e da concorrência distintas, possuem com- petências diferentes e inserem-se em
competencies through the acquisition of companies and the fostering of startups in business incubator hubs.
To progress, in addition to con- tinuing efforts in innovation, these companies must broaden their range of technological assets and co-lead in- novative ecosystems. These ecosystems are formed of interdisciplinary and international networks of universities, research centers and companies.
Public-private cooperation is essen- tial, which requires building consensus between the parties; implementing actions through programs with a focus on challenges; the coordinated action of funding and regulatory agencies is also essential. In addition to public funding using all the available instru- ments, such as subsidies, credit and
venture capital, to support the entire innovation cycle, the co-participation of the private sector in sharing risks is essential. The regulations should be geared towards innovations that exploit technological frontiers and public procurement should be focused on priority programs and associated with new technologies.
Companies that can keep pace with the productivity frontier are also distributed across the country and are mostly (in terms of production value) in sectors related to commodities. The strategy is to invest in integrated, connected and intelligent business models, covering the entire value chain, to drive productivity gains and sustain international competitiveness. For these companies, the core skills
are engineering, R&D, knowledge of markets to capture opportunities for product/service differentiation and investing (corporate venturing) in technology-based companies.
Special attention must be given to developing new materials and ad- vanced digital solutions. Innovation ecosystems must evolve into interdis- ciplinary networks. With regard to funding, it will be essential to organize public funding in programs which share risks with the private sector. The regulations must ensure precision, quality, security (including of data) and environmental sustainability.
In companies that need to shorten distances from the productive frontier, the smaller ones predominate. To progress, it is necessary to invest in
36