Page 48 - Basic PD Theory
P. 48
PD Investigations
outside surface of the copper stack (and adjacent to the ground insulation), PD will not be a symptom of turn failure due to voltage surges. As with
internal delamination, there tends to be an inverse temperature effect. If the voids are large, it is possible for the negative PD to
increase with load due to the higher conductor vibration associated with the higher mechanical forces.
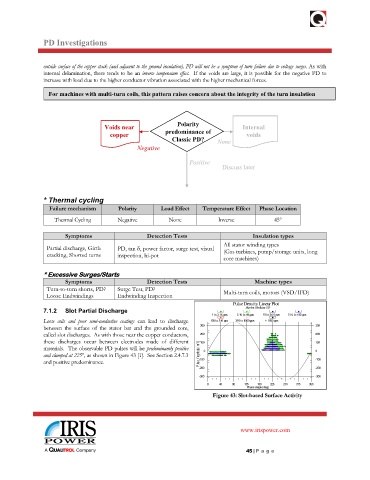
For machines with multi-turn coils, this pattern raises concern about the integrity of the turn insulation
I
Voids near Polarity Internal nternal
copper predominance of voi
voidsds
Classic PD? None
None
Negative
Positivesitive
Po
Discuss laterscuss later
Di
* Thermal cycling
Failure mechanism Polarity Load Effect Temperature Effect Phase Location
Thermal Cycling Negative None Inverse 45°
Symptoms Detection Tests Insulation types
All stator winding types
Partial discharge, Girth PD, tan δ, power factor, surge test, visual (Gas turbines, pump/storage units, long
cracking, Shorted turns inspection, hi-pot
core machines)
* Excessive Surges/Starts
Symptoms Detection Tests Machine types
Turn-to-turn shorts, PD? Surge Test, PD?
Loose Endwindings Endwinding Inspection Multi-turn coils, motors (VSD/IFD)
Pulse Density Linear Plot
7.1.2 Slot Partial Discharge Bipolar Machine PD
1 to 3.16 pps 3.16 to 10 pps 10 to 31.6 pps 31.6 to 100 pps
Loose coils and poor semi-conductive coatings can lead to discharge 100 to 316 pps 316 to 1000 pps > 1000 pps
between the surface of the stator bar and the grounded core, 300 300
called slot discharges. As with those near the copper conductors, 200 200
these discharges occur between electrodes made of different 100 100
materials. The observable PD pulses will be predominantly positive 0 0
and clumped at 225°, as shown in Figure 43 [1]. See Section 2.4.7.3 Pulse Magnitude [mV]
and positive predominance. -100 -100
-200 -200
-300 -300
0 45 90 135 180 225 270 315 360
Phase Angle [deg]
Figure 43: Slot-based Surface Activity
www.irispower.com
45 | P ag e