Page 63 - Basic PD Theory
P. 63
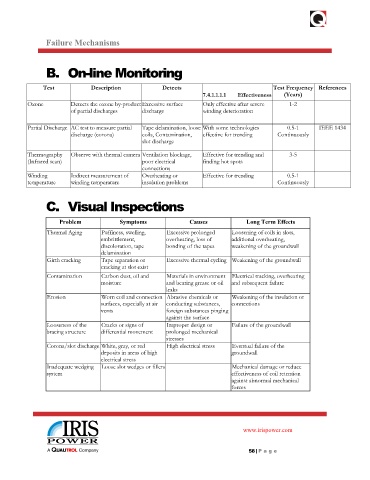
Failure Mechanisms
B. On-line Monitoring
Test Description Detects Test Frequency References
7.4.1.1.1.1 Effectiveness (Years)
Ozone Detects the ozone by-product Excessive surface Only effective after severe 1-2
of partial discharges discharge winding deterioration
Partial Discharge AC test to measure partial Tape delamination, loose With some technologies 0.5-1 IEEE 1434
discharge (corona) coils, Contamination, effective for trending Continuously
slot discharge
Thermography Observe with thermal camera Ventilation blockage, Effective for trending and 3-5
(Infrared scan) poor electrical finding hot spots
connections
Winding Indirect measurement of Overheating or Effective for trending 0.5-1
temperature winding temperature insulation problems Continuously
C. Visual Inspections
Problem Symptoms Causes Long Term Effects
Thermal Aging Puffiness, swelling, Excessive prolonged Loosening of coils in slots,
embrittlement, overheating, loss of additional overheating,
discoloration, tape bonding of the tapes weakening of the groundwall
delamination
Girth cracking Tape separation or Excessive thermal cycling Weakening of the groundwall
cracking at slot exist
Contamination Carbon dust, oil and Materials in environment Electrical tracking, overheating
moisture and bearing grease or oil and subsequent failure
leaks
Erosion Worn coil and connection Abrasive chemicals or Weakening of the insulation or
surfaces, especially at air conducting substances, connections
vents foreign substances pinging
against the surface
Looseness of the Cracks or signs of Improper design or Failure of the groundwall
bracing structure differential movement prolonged mechanical
stresses
Corona/slot discharge White, gray, or red High electrical stress Eventual failure of the
deposits in areas of high groundwall
electrical stress
Inadequate wedging Loose slot wedges or fillers Mechanical damage or reduce
system effectiveness of coil retention
against abnormal mechanical
forces
www.irispower.com
58 | P ag e