Page 81 - Basic PD Theory
P. 81
References
delamination ⇒ ∆ tan δ increases
moisture Contamination ⇒ tan δ increases
Typically the DF for epoxy mica windings is about 0.5% and for asphaltic mica windings it is 3 to 5%. Trending the results
against time makes the best use of this test. As with the ∆ capacitance test, voltage stress coatings can lead to ambiguous results
obtained at high voltage.
Finds: moisture and delaminated insulation
3. Power Factor (cos θ) IEEE Std 286:
Similar to the dissipation factor (tan δ) the power factor test is looking for any changes in the Recommended Practice for
insulation system of the winding. The test is normally done at a specific applied voltage that Measurement of Power-
makes it possible for comparing the results to other machines. This is a valuable test for Factor Tip-Up of Rotating
determining the extent of curing in new coils or winding. Because the presence of the voltage Machinery Stator Coil
Insulation
stress control in a complete winding greatly affects the results, tests on complete windings can be
ambiguous.
X
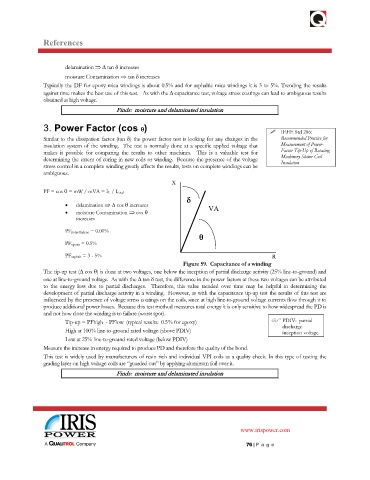
PF = cos θ = mW / mVA = I L / I total
δ
• delamination ⇒ ∆ cos θ increases VA
• moisture Contamination ⇒ cos θ
increases
PF polyethylene = 0.01%
θ
PF epoxy = 0.5%
PF asphalt = 3 - 5% R
Figure 59. Capacitance of a winding
The tip-up test (∆ cos θ) is done at two voltages, one below the inception of partial discharge activity (25% line-to-ground) and
one at line-to-ground voltage. As with the ∆ tan δ test, the difference in the power factors at these two voltages can be attributed
to the energy loss due to partial discharges. Therefore, this value trended over time may be helpful in determining the
development of partial discharge activity in a winding. However, as with the capacitance tip-up test the results of this test are
influenced by the presence of voltage stress coatings on the coils, since at high line-to-ground voltage currents flow through it to
produce additional power losses. Because this test method measures total energy it is only sensitive to how widespread the PD is
and not how close the winding is to failure (worst spot).
Tip-up = PFhigh - PFlow (typical results: 0.5% for epoxy) PDIV: partial
High at 100% line-to-ground rated voltage (above PDIV) discharge
inception voltage.
Low at 25% line-to-ground rated voltage (below PDIV)
Measure the increase in energy required to produce PD and therefore the quality of the bond.
This test is widely used by manufacturers of resin rich and individual VPI coils as a quality check. In this type of testing the
grading layer on high voltage coils are “guarded out” by applying aluminum foil over it.
Finds: moisture and delaminated insulation
www.irispower.com
76 | P ag e