Page 125 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 125
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology
(MD303)
❖ Manifestations
• Many renal calculi are asymptomatic until they obstruct kidney structures such as the calyces or
pelves.
• Severe pain that can result from obstruction
• Fever, chills
• Hematuria
• Gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, vomiting)
• Urine obstruction
❖ Complications that may include
• Damage to renal structures
• Acute renal failure.
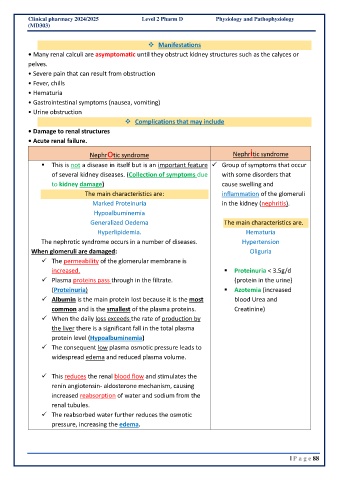
Nephrotic syndrome Nephritic syndrome
▪ This is not a disease in itself but is an important feature ✓ Group of symptoms that occur
of several kidney diseases. (Collection of symptoms due with some disorders that
to kidney damage) cause swelling and
The main characteristics are: inflammation of the glomeruli
Marked Proteinuria in the kidney (nephritis).
Hypoalbuminemia
Generalized Oedema The main characteristics are.
Hyperlipidemia. Hematuria
The nephrotic syndrome occurs in a number of diseases. Hypertension
When glomeruli are damaged: Oliguria
✓ The permeability of the glomerular membrane is
increased. ▪ Proteinuria < 3.5g/d
✓ Plasma proteins pass through in the filtrate. (protein in the urine)
(Proteinuria) ▪ Azotemia (increased
✓ Albumin is the main protein lost because it is the most blood Urea and
common and is the smallest of the plasma proteins. Creatinine)
✓ When the daily loss exceeds the rate of production by
the liver there is a significant fall in the total plasma
protein level (Hypoalbuminemia)
✓ The consequent low plasma osmotic pressure leads to
widespread edema and reduced plasma volume.
✓ This reduces the renal blood flow and stimulates the
renin angiotensin- aldosterone mechanism, causing
increased reabsorption of water and sodium from the
renal tubules.
✓ The reabsorbed water further reduces the osmotic
pressure, increasing the edema.
| P a g e 88