Page 162 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 162
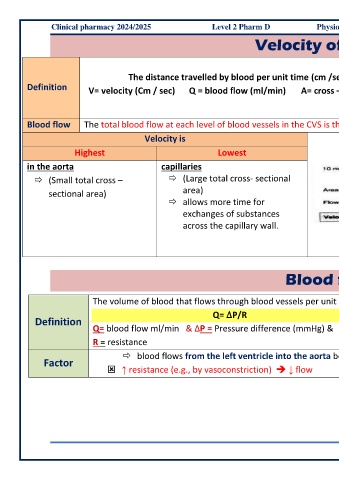
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
Velocity of blood flow
Velocity ➔ directly proportional to blood
The distance travelled by blood per unit time (cm /sec) ➔ V= Q/A flow
Definition V= velocity (Cm / sec) Q = blood flow (ml/min) A= cross – sectional area (Cm3) Velocity ➔ inversely proportional to total
cross-sectional area at any level of the CVS
Blood flow The total blood flow at each level of blood vessels in the CVS is the same and is equal to the cardiac output
Velocity is
Highest Lowest
in the aorta capillaries
(Small total cross – (Large total cross- sectional
sectional area) area)
allows more time for
exchanges of substances
across the capillary wall.
Blood flow (Q)
The volume of blood that flows through blood vessels per unit time. directly proportional to the pressure difference between the
Q= ∆P/R two ends of the vessel [Blood flows from high to low
Definition
Q= blood flow ml/min & ∆P = Pressure difference (mmHg) & pressure]
R = resistance inversely proportional to the resistance of vessels
blood flows from the left ventricle into the aorta because pressure in the ventricle is higher than pressure in the aorta.
Factor
↑ resistance (e.g., by vasoconstriction) ➔ ↓ flow ** ↓resistance (e.g. by vasodilation) ➔ ↑ flow
| P a g e 109