Page 158 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 158
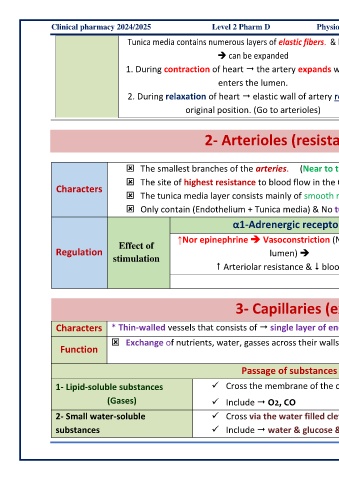
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
Tunica media contains numerous layers of elastic fibers. & less Muscle
➔ can be expanded
* Contain a thicker layer of smooth muscle in the tunica
1. During contraction of heart the artery expands when blood
media
enters the lumen.
2. During relaxation of heart elastic wall of artery recoil to its
original position. (Go to arterioles)
2- Arterioles (resistance vessels) “small +resist +SM"
The smallest branches of the arteries. (Near to the tissue and away from heart)
The site of highest resistance to blood flow in the CVS (resistance vessels) هيف مكحتي ردقي مسجلاو تلاضع اهرادج نلا
Characters
The tunica media layer consists mainly of smooth muscle ➔ so body control its diameter by sympathetic nervous system.
Only contain (Endothelium + Tunica media) & No tunica externa
α1-Adrenergic receptors β2-Adrenergic receptors
↑Nor epinephrine ➔ Vasoconstriction (Narrowing of the ↓Nor epinephrine ➔ Vasodilatation (Widening of the
Effect of
Regulation lumen) ➔ lumen) ➔
stimulation
Arteriolar resistance & blood flow Arteriolar resistance & blood flow
α1 effect is the predominant
3- Capillaries (exchange vessels)
Characters * Thin-walled vessels that consists of single layer of endothelial cells. ➔ facilitate exchange
Exchange of nutrients, water, gasses across their walls. Link between arterioles (oxygenated blood) with Venules (no
Function
oxygenated)
Passage of substances across the capillary wall
1- Lipid-soluble substances ✓ Cross the membrane of the capillary endothelial cells by simple diffusion. ةقاط يأ يرغ نم طيسبلا راشتنلاا
(Gases) ✓ Include O2, CO
2- Small water-soluble ✓ Cross via the water filled clefts (gaps or pores) between the endothelial cells.
substances ✓ Include water & glucose & amino acids.
| P a g e 107