Page 191 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 191
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
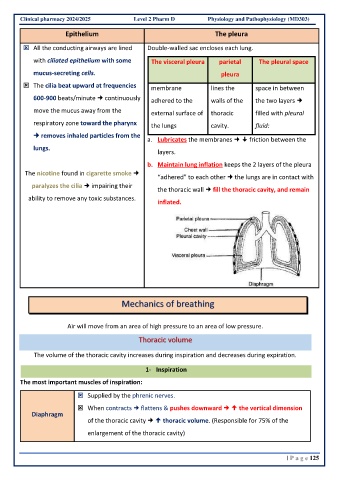
Epithelium The pleura
All the conducting airways are lined Double-walled sac encloses each lung.
with ciliated epithelium with some The visceral pleura parietal The pleural space
mucus-secreting cells. pleura
The cilia beat upward at frequencies membrane lines the space in between
600-900 beats/minute continuously adhered to the walls of the the two layers
move the mucus away from the external surface of thoracic filled with pleural
respiratory zone toward the pharynx the lungs cavity. fluid:
removes inhaled particles from the
a. Lubricates the membranes friction between the
lungs.
layers.
b. Maintain lung inflation keeps the 2 layers of the pleura
The nicotine found in cigarette smoke
“adhered” to each other the lungs are in contact with
paralyzes the cilia impairing their
the thoracic wall fill the thoracic cavity, and remain
ability to remove any toxic substances.
inflated.
Mechanics of breathing
Air will move from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure.
Thoracic volume
The volume of the thoracic cavity increases during inspiration and decreases during expiration.
1- Inspiration
The most important muscles of inspiration:
Supplied by the phrenic nerves.
When contracts flattens & pushes downward the vertical dimension
Diaphragm
of the thoracic cavity thoracic volume. (Responsible for 75% of the
enlargement of the thoracic cavity)
| P a g e 125