Page 193 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 193
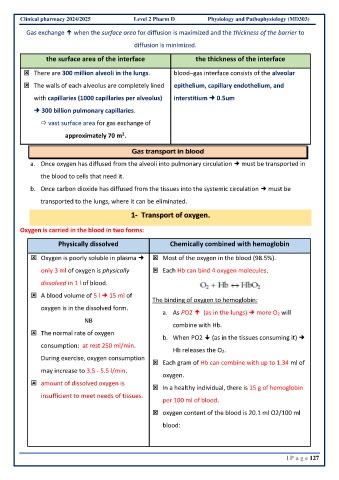
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
Gas exchange when the surface area for diffusion is maximized and the thickness of the barrier to
diffusion is minimized.
the surface area of the interface the thickness of the interface
There are 300 million alveoli in the lungs. blood–gas interface consists of the alveolar
The walls of each alveolus are completely lined epithelium, capillary endothelium, and
with capillaries (1000 capillaries per alveolus) interstitium 0.5um
300 billion pulmonary capillaries.
vast surface area for gas exchange of
2
approximately 70 m .
Gas transport in blood
a. Once oxygen has diffused from the alveoli into pulmonary circulation must be transported in
the blood to cells that need it.
b. Once carbon dioxide has diffused from the tissues into the systemic circulation must be
transported to the lungs, where it can be eliminated.
1- Transport of oxygen.
Oxygen is carried in the blood in two forms:
Physically dissolved Chemically combined with hemoglobin
Oxygen is poorly soluble in plasma Most of the oxygen in the blood (98.5%).
only 3 ml of oxygen is physically Each Hb can bind 4 oxygen molecules.
dissolved in 1 l of blood.
A blood volume of 5 l 15 ml of
The binding of oxygen to hemoglobin:
oxygen is in the dissolved form.
a. As PO2 (as in the lungs) more O2 will
NB
combine with Hb.
The normal rate of oxygen
b. When PO2 (as in the tissues consuming it)
consumption: at rest 250 ml/min.
Hb releases the O2.
During exercise, oxygen consumption
Each gram of Hb can combine with up to 1.34 ml of
may increase to 3.5 - 5.5 l/min.
oxygen.
amount of dissolved oxygen is
In a healthy individual, there is 15 g of hemoglobin
insufficient to meet needs of tissues.
per 100 ml of blood.
oxygen content of the blood is 20.1 ml O2/100 ml
blood:
| P a g e 127