Page 135 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 135
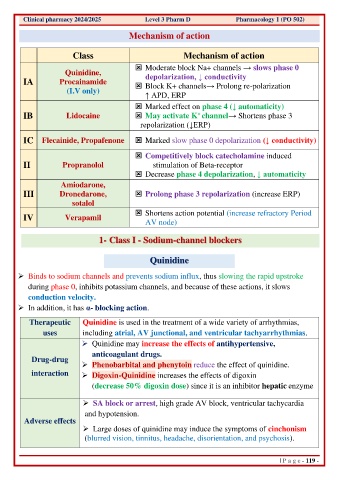
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
Mechanism of action
Class Mechanism of action
Moderate block Na+ channels → slows phase 0
Quinidine, depolarization, ↓ conductivity
IA Procainamide Block K+ channels→ Prolong re-polarization
(I.V only)
↑ APD, ERP
Marked effect on phase 4 (↓ automaticity)
IB Lidocaine May activate K channel→ Shortens phase 3
+
repolarization (↓ERP)
IC Flecainide, Propafenone Marked slow phase 0 depolarization (↓ conductivity)
Competitively block catecholamine induced
II Propranolol stimulation of Beta-receptor
Decrease phase 4 depolarization, ↓ automaticity
Amiodarone,
III Dronedarone, Prolong phase 3 repolarization (increase ERP)
sotalol
Shortens action potential (increase refractory Period
IV Verapamil
AV node)
1- Class I - Sodium-channel blockers
Quinidine
➢ Binds to sodium channels and prevents sodium influx, thus slowing the rapid upstroke
during phase 0, inhibits potassium channels, and because of these actions, it slows
conduction velocity.
➢ In addition, it has α- blocking action.
Therapeutic Quinidine is used in the treatment of a wide variety of arrhythmias,
uses including atrial, AV junctional, and ventricular tachyarrhythmias.
➢ Quinidine may increase the effects of antihypertensive,
anticoagulant drugs.
Drug-drug
➢ Phenobarbital and phenytoin reduce the effect of quinidine.
interaction ➢ Digoxin-Quinidine increases the effects of digoxin
(decrease 50% digoxin dose) since it is an inhibitor hepatic enzyme
➢ SA block or arrest, high grade AV block, ventricular tachycardia
and hypotension.
Adverse effects
➢ Large doses of quinidine may induce the symptoms of cinchonism
(blurred vision, tinnitus, headache, disorientation, and psychosis).
| P a g e - 119 -