Page 186 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 186
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
Platelet activating factor (PAF)
• PAF is a phospholipid-derived mediator released by the action of phospholipase A2
from activated inflammatory cells.
• It causes VD, increase vascular permeability, chemotaxis, and activation of leukocyte,
activation and aggregation of platelet, and smooth muscle contraction.
• It is potent Pathophysiological mediator of asthma and shock
• significant role as chemoattractant for eosinophils (eosinophile higher levels in
Asthma)
• Lexipafant is PAF antagonist, used in cases of Pancreatitis.
Vasoactive peptides
● Several peptides exert important direct effects on vascular and other smooth muscles.
● These peptides include:
➢ Vasoconstrictors (angiotensin II, vasopressin, endothelin)
➢ Vasodilators (bradykinin and related kinins, natriuretic peptides, substance P).
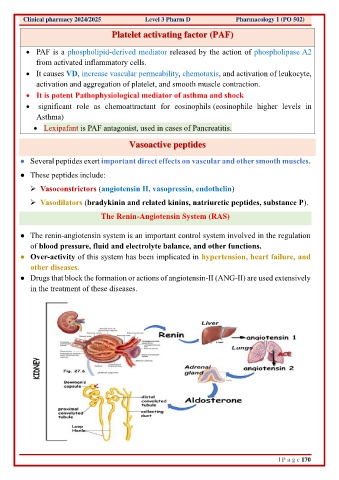
The Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS)
● The renin-angiotensin system is an important control system involved in the regulation
of blood pressure, fluid and electrolyte balance, and other functions.
● Over-activity of this system has been implicated in hypertension, heart failure, and
other diseases.
● Drugs that block the formation or actions of angiotensin-II (ANG-II) are used extensively
in the treatment of these diseases.
| P a g e 170